Decoding CBC vs CMP: Key Differences Unveiled
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) and a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) are both common blood tests used to assess overall health, but they measure different components and provide distinct information. Here's a comparison of cbc vs cmp:
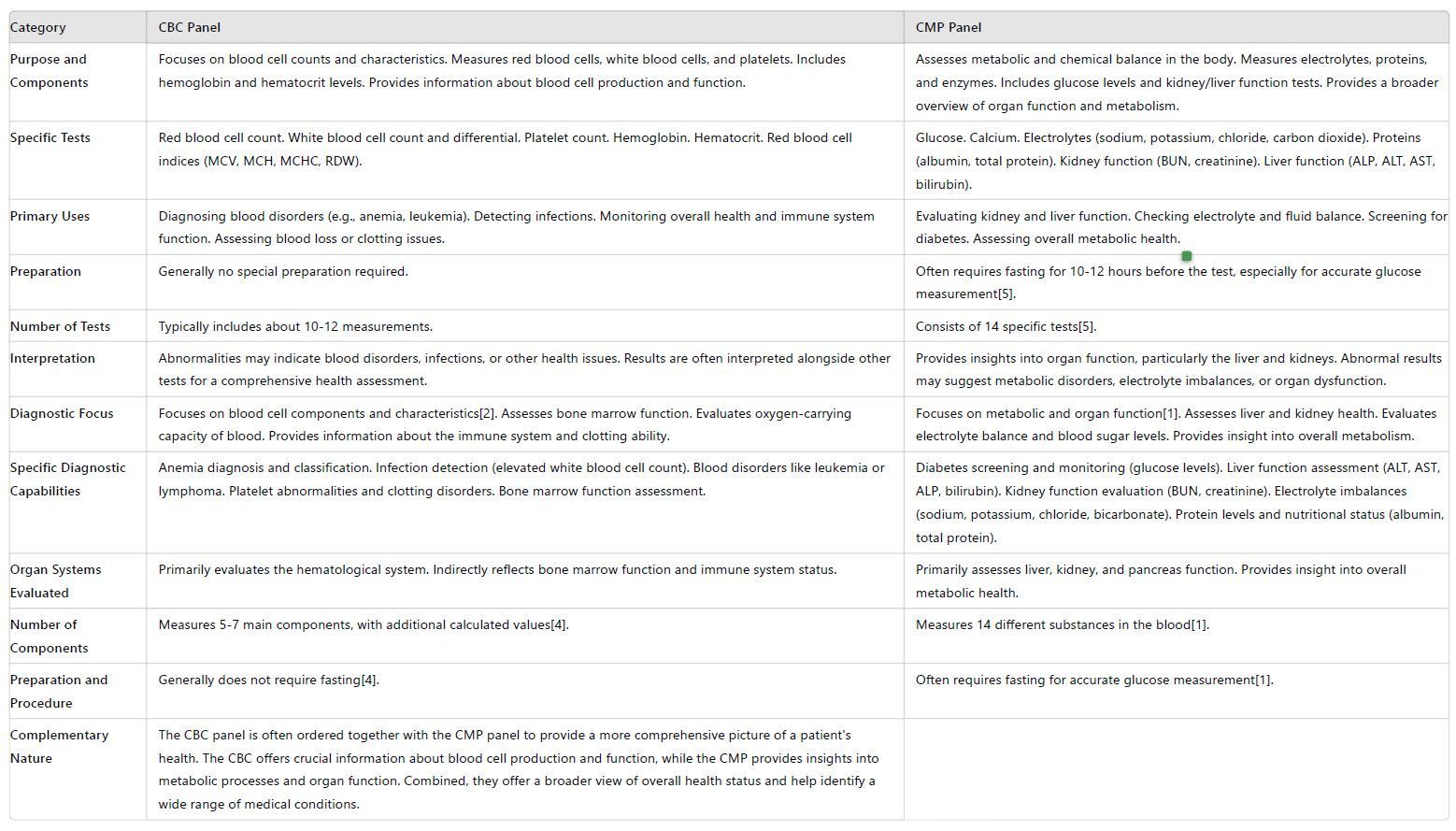
Purpose and Components
CBC Panel:
- Focus: Blood cell counts and characteristics
- Measures: Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
- Includes: Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels
- Provides: Information about blood cell production and function
CMP Panel:
- Assesses: Metabolic and chemical balance in the body
- Measures: Electrolytes, proteins, and enzymes
Includes: Glucose levels and kidney/liver function tests
- Provides: A broader overview of organ function and metabolism
Specific Tests
- Red blood cell count
- White blood cell count and differential
- Platelet count
- Hemoglobin
- Hematocrit
Red blood cell indices (MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW)
- Glucose
- Calcium
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride, and carbon dioxide)
- Proteins (albumin, total protein)
Kidney function (BUN, creatinine)
- Liver function (ALP, ALT, AST, bilirubin)
Primary Uses
- Diagnosing blood disorders (e.g., anemia, leukemia)
- Detecting infections
- Monitoring overall health and immune system function
- Assessing blood loss or clotting issues
- Evaluating kidney and liver function
- Checking electrolyte and fluid balance
- Screening for diabetes
- Assessing overall metabolic health
Preparation
- Generally no special preparation required
- Often requires fasting for 10-12 hours before the test, especially for accurate glucose measurement [5]
Number of Tests
- Typically includes about 10-12 measurements
- Consists of 14 specific tests[5]
Interpretation
- Abnormalities may indicate blood disorders, infections, or other health issues
- Results are often interpreted alongside other tests for a comprehensive health assessment
- Provides insights into organ function, particularly the liver and kidneys
- Abnormal results may suggest metabolic disorders, electrolyte imbalances, or organ dysfunction
In summary, while both tests are valuable for assessing overall health, the CBC focuses on blood cell components and related disorders, while the CMP provides a broader view of metabolic function and organ health. Healthcare providers often use these tests in combination for a more comprehensive evaluation of a patient's health status.
Diagnostic Focus
- Focuses on: Metabolic and organ function[1]
- Assesses: Liver and kidney health
- Evaluates: Electrolyte balance and blood sugar levels
- Provides: Insight into overall metabolism
- Concentrates on: Blood cell components and characteristics[2]
- Assesses: Bone marrow function
- Evaluates: Oxygen-carrying capacity of blood
- Provides: Information about the immune system and clotting ability

Specific Diagnostic Capabilities
- Diabetes screening and monitoring (glucose levels)
- Liver function assessment (ALT, AST, ALP, bilirubin)
- Kidney function evaluation (BUN, creatinine)
- Electrolyte imbalances (sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate)
- Protein levels and nutritional status (albumin, total protein)
Anemia diagnosis and classification
- Infection detection (elevated white blood cell count)
- Blood disorders like leukemia or lymphoma
- Platelet abnormalities and clotting disorders
- Bone marrow function assessment
Organ Systems Evaluated
- Primarily assesses liver, kidney, and pancreas function
- Provides insight into overall metabolic health
- Primarily evaluates the hematological system
- Indirectly reflects bone marrow function and immune system status
Number of Components
- Measures 14 different substances in the blood [1]
- Typically includes 5-7 main components, with additional calculated values [4]
Preparation and Procedure
- Often requires fasting for accurate glucose measurement [1]
- Generally does not require fasting [4]
CBC vs CMP: Complementary Nature
While the CMP and CBC panels differ in their focus, they are often ordered together to provide a more comprehensive picture of a patient's health. The CMP offers insight into metabolic processes and organ function, while the CBC provides crucial information about blood cell production and function. Together, they offer a broader view of overall health status and can help identify a wide range of medical conditions.
In summary, the CMP panel is better suited for assessing metabolic health, liver and kidney function, and electrolyte balance, while the CBC panel excels in diagnosing blood disorders, infections, and evaluating overall blood cell health. Both tests are valuable tools in medical diagnostics, often used in conjunction to provide a more complete health assessment.
Citations
- Complete Blood Count - Wikipedia
- Complete Blood Count - Mayo Clinic
- Complete Blood Count - Labcorp
- Comprehensive Metabolic Panel - Wikipedia
- Comprehensive Metabolic Panel - Cleveland Clinic
- How to Read Comprehensive Metabolic Panel - Kidney Foundation
- Comprehensive Metabolic Panel - MedlinePlus
- Comprehensive Metabolic Panel - Testing.com
- Complete Blood Count - Testing.com
- Complete Blood Count - WebMD





