Low Anion Gap Demystified: Interpret Your Blood Test Result
Are you due for a blood test and have heard about the anion gap test but are unsure of what it is? The anion gap blood test, also known as the serum anion gap test, is a common medical test that measures the levels of electrolytes in the blood. It helps identify any imbalances in electrolyte levels, including acid levels, which can indicate various health conditions such as kidney disease, diabetes, or metabolic acidosis. In this blog post, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about the anion gap blood test, including its importance, common causes of abnormal results, and how to prepare for it. We’ll also cover how to interpret the results and where you can buy the test at discounted prices. So if you’re curious about your health and want to learn more about this important diagnostic tool, keep reading!
Anion Gap Blood Test: Overview
The anion gap blood test measures the difference in electrical charge between positively charged cations and negatively charged anions found in the blood. It is used to evaluate the acid-base balance and help detect certain medical conditions. Typically, the test is included in a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) or basic metabolic panel (BMP). Healthcare providers rely on the results of this test to diagnose and monitor electrolyte imbalances. Understanding the anion gap, including the role of chloride as a negatively charged anion, can provide valuable insights into overall health. Other factors, such as lithium, can also affect the calculation of the anion gap. For example, in high concentrations, lithium can lower the anion gap.
What is the Anion Gap?
The anion gap is a calculation that measures the difference between cations and anions in the blood. It gives insight into the presence of unmeasured ions or substances. The normal range for anion gap is 8 to 16 mEq/L, and abnormal levels may indicate underlying health conditions.
Symptoms of an Electrolyte Imbalance
Anion gap blood test is used to measure the levels of electrolytes in the blood. Electrolytes are minerals that help regulate various functions in the body, such as muscle and nerve function, hydration, and blood pH levels. An imbalance in electrolytes can cause several symptoms like muscle weakness, fatigue, an irregular heartbeat, confusion, seizures, and nausea. The anion gap blood test can help diagnose these imbalances so that appropriate treatment can be given to restore normal electrolyte levels and prevent further complications.
Finding an Electrolyte Panel Test
The anion gap blood test is a type of electrolyte panel test that can help diagnose certain medical conditions. Electrolytes are minerals in your body that help regulate important bodily functions like muscle contractions and nerve impulses. An electrolyte panel test measures the levels of different electrolytes in your blood, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate. The anion gap specifically measures the balance between positively charged ions (like sodium and positive electric charge) and negatively charged ions (like chloride and bicarbonate) in your blood, which is crucial for maintaining proper electrolyte balance. This anion gap measurement is based on the results of individual electrolyte blood tests, which are commonly included in routine bloodwork panels. By analyzing these levels, doctors can identify imbalances that may be indicative of medical issues such as kidney disease, diabetes, or poisoning.
How to Calculate the Anion Gap from a CMP test
The anion gap is the difference between the amounts of cations (ions with a positive charge, like Na+ and K+) and anions (ions with a negative charge, like Cl- and HCO3-). This information comes from the comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP). There are three types: serum, plasma, and urine anion gaps. The most common application of the anion gap is classifying cases of metabolic acidosis, states of lower than normal blood pH. Specifically, classifying into either those that do or those that do not have unmeasured anions in the plasma. The human body is electrically neutral; therefore, in reality, it does not have a true anion gap. However, the madias ne anion gap calculator, a useful tool in clinical medicine, can be used to calculate the difference and identify potential imbalances. The calculation then finds utility in exposing variations in that balance.
Calculation relies on measuring specific cations, Na+ and K+ and specific anions, Cl- and HCO3-. The equation is as follows: (Na+ + K+) – (Cl- + HCO3-) = Anion Gap. The anion gap formula can be manipulated to expose the presence of unmeasured cations and anions, as shown below.
Why is the Anion Gap Important in a Blood Test?
The anion gap plays a crucial role in blood tests as it helps assess acid-base balance. It can indicate the presence of metabolic acidosis, offering insight into conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis. Monitoring the anion gap is vital for evaluating treatment effectiveness and managing various health conditions.
What are the Common Causes of a Low Anion Gap?
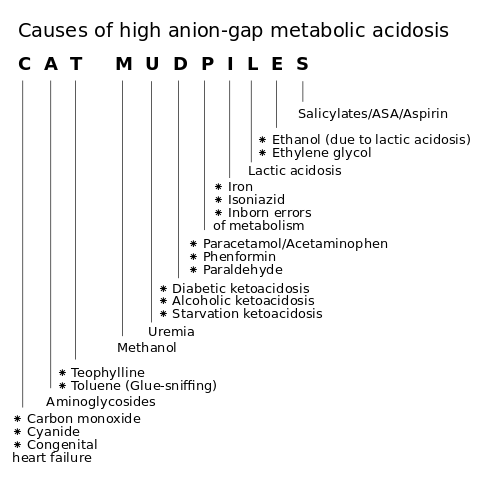
An abnormal anion gap can be attributed to various factors, including conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, kidney disease, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. On the other hand, hypoalbuminemia or certain medications may be the cause, including ethylene glycol (antifreeze) poisoning. Understanding the root cause of an abnormal anion gap is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Restoring normal anion gap levels involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause.
A low anion gap is a rare condition that can be caused by a variety of factors [1] [2] [3]. Some of the most common causes of low anion gap include:
- Hypoalbuminemia: This involves having too little of an essential protein called albumin in the blood. Hypoalbuminemia usually occurs because of inflammation throughout the body. Specific causes of hypoalbuminemia include sepsis, recent surgery, malnutrition, severe burns, liver or kidney disease, hyperkalemia, which is high potassium, and hypercalcemia, which is high calcium [2].
- Lab error: A low anion gap value is very rare and may be due to laboratory error. If your test indicates a low anion gap value, your doctor may order a second test to account for laboratory error [3].
- Multiple myeloma: A low anion gap level is rare and indicates an abnormally high level of positively charged molecules. The most common cause of this is multiple myeloma, a cancer of a class of white blood cells called plasma cells. Typically, plasma cells help our bodies fight infections. In multiple myeloma, cancerous plasma cells accumulate in the bone marrow and crowd out healthy blood cells. The cancerous cells then produce abnormal proteins that cause kidney problems.
- Hypoalbuminemia: This involves having too little of an essential protein called albumin in the blood. Hypoalbuminemia usually occurs because of inflammation throughout the body. Specific causes of hypoalbuminemia include sepsis, recent surgery, malnutrition, severe burns, liver or kidney disease, hyperkalemia, which is high potassium, and hypercalcemia, which is high calcium [2].
- Lab error: A low anion gap value is very rare and may be due to laboratory error. If your test indicates a low anion gap value, your doctor may order a second test to account for laboratory error [3].
- Multiple myeloma: A low anion gap level is rare and indicates an abnormally high level of positively charged molecules. The most common cause of this is multiple myeloma, a cancer of a class of white blood cells called plasma cells. Typically, plasma cells help our bodies fight infections. In multiple myeloma, cancerous plasma cells accumulate in the bone marrow and crowd out healthy blood cells. The cancerous cells then produce abnormal proteins that cause kidney problems.
If you have a low anion gap, your doctor will use the results of the anion gap test, your medical history, and other tests to make a diagnosis. A low anion gap test result may indicate alkalosis or a low level of albumin, a protein in the blood. However, this result is rare and your provider may have you tested again to confirm its accuracy. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider if you have any concerns about your anion gap test results [1] or [3]. Additionally, understanding laboratory tests, reference ranges, and interpreting results can provide valuable insight into the potential causes of a low anion gap.
Hypoalbuminemia
The anion gap blood test is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the acid-base balance in the body. One of the conditions that can be detected through this test is hypoalbuminemia, which is a low level of albumin in the blood. The liver produces albumin, a protein that is in charge of carrying fatty acids, hormones, and medications throughout the body. A low level of albumin, also known as low albumin, can indicate underlying health conditions such as liver disease or malnutrition and can lead to complications such as edema or impaired wound healing. If your blood results reveal a low anion gap, it may mean you have a lower-than-normal level of albumin (hypoalbuminemia). Albumin is an essential protein in your blood and understanding your results is crucial to developing an appropriate treatment plan for your individual health needs.
Lithium Can Increase Anion Gap
The anion gap blood test is a common diagnostic tool used to measure the balance of electrolytes in the body. Lithium, a medication commonly used to treat bipolar disorder, can affect the results of this test. Lithium can increase the anion gap by decreasing chloride levels and increasing bicarbonate levels. Therefore, it is important to notify your healthcare provider if you are taking lithium before undergoing an anion gap blood test to ensure accurate results, as a reduced anion gap may be falsely reported due to the interference of lithium.
Anion Gap Blood Test vs. Other Tests
The anion gap blood test differs from comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) or basic metabolic panel (BMP) by providing specific information about electrolytes and acid-base balance. While CMP and BMP offer a broader overview of overall health, the anion gap test hones in on these specific parameters. It complements other tests and aids in diagnosing certain medical conditions. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine which tests are necessary based on individual health needs.
How is the Anion Gap Blood Test Different from Other Blood Tests?
The anion gap blood test stands apart from other blood tests by specifically measuring the difference between positively and negatively charged ions. Unlike comprehensive metabolic panels (CMP) or basic metabolic panels (BMP), which include additional parameters, the anion gap focuses on electrolyte levels to provide a more targeted analysis. This understanding helps healthcare providers tailor diagnostic approaches for individual patients by calculating the anion gap from the results of an electrolyte panel, another type of blood test. A note from the Cleveland Clinic: If your anion gap test is part of a routine bloodwork panel, such as a basic metabolic panel, it could take one to two business days before you get the results. Seeing an abnormal test result can be stressful. Know that having a high or low anion gap doesn’t necessarily mean you have a medical condition and need treatment.
When is the Anion Gap Blood Test Recommended?
The anion gap blood test is recommended in various clinical situations, such as suspected metabolic acidosis or toxicities. It may be ordered for individuals with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or altered mental status. Healthcare providers determine the appropriateness based on individual circumstances and routine monitoring of electrolyte imbalances.
Preparing for the Anion Gap Blood Test
To ensure accurate and reliable results from the anion gap blood test, it is important to follow specific preparation instructions provided by your healthcare provider. This may include fasting for a certain period of time before the test and informing your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking, as well as any underlying health conditions or symptoms that may impact the results. It is also important to note that during the test, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube for analysis, also known as a blood sample. Adhering to these guidelines, including any special instructions, will help ensure that you receive accurate and reliable test results.
What Should You Do Before Taking the Anion Gap Blood Test?
Before undergoing the anion gap blood test, it's important to follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding fasting. Avoid consuming food or beverages for the specified duration, but do stay hydrated by drinking water unless instructed otherwise. Inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you're taking, and reach out to them if you have any questions or concerns.
What Should You Avoid Before Taking the Anion Gap Blood Test?
During the fasting period before the test, avoid consuming anything except water. Steer clear of alcohol or caffeine, as they can affect the accuracy of the results. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding medications and supplements that may interfere with the test. For specific guidance, consult your healthcare provider. Adhering to these guidelines ensures accurate test results.
Interpreting the Results of the Anion Gap Blood Test
The anion gap blood test provides important information about the balance of electrolytes in your body, specifically in your plasma. A normal anion gap ranges from 3 to 11 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L), depending on the reference ranges used by the laboratory. If the anion gap is high, it may indicate metabolic acidosis, which is a condition where there is too much acid in the blood. On the other hand, a low anion gap could suggest an underlying health condition. It is crucial to have the results interpreted by a healthcare professional, as further tests may be needed to determine the cause and understand the clinical picture, especially if there is a high anion gap test result. Electrolytes are elements and compounds that occur naturally in the body and control important physiological functions. Calcium, chloride, magnesium, and sodium, among others, are electrolytes.
How to Buy the Anion Gap Blood Test on DiscountedLabs.com
To purchase the Anion Gap Blood Test on DiscountedLabs.com, simply visit their website and navigate to the menu where you can choose the test. Provide the required information and make the payment. Afterward, you will receive a lab order form via email. Take this form to a participating lab for sample collection. It's a straightforward process that allows you to conveniently order the Anion Gap Blood Test, which is included in a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP).
Frequently Asked Questions
Does high anion gap mean diabetes?
A high anion gap does not necessarily indicate diabetes. It can be a sign of metabolic acidosis or kidney disease. While diabetes is associated with a higher risk of metabolic acidosis, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan.
What does it mean when your anion gap is high?
A high anion gap in a blood test may be a sign of metabolic acidosis, which can result from conditions like kidney disease, diabetes, or lactic acidosis. Further tests are usually needed to determine the underlying cause, and treatment will depend on that cause.
What does it mean when your anion gap is low?
When your anion gap is low, it could indicate an electrolyte imbalance or metabolic acidosis. The normal range for anion gap varies between labs, but generally, a low level is below 7 mEq/L. Consult with your healthcare provider to understand your individual results and treatment options.
What are the normal ranges for anion gap levels in a blood test?
The normal range for anion gap levels in a blood test is typically between 3 and 10 mEq/L. However, there is a wide range of normal values, often between 8 to 10 mEq/L, which means an increase in anion concentration can be present even in the absence of an increased anion gap. Abnormal levels may suggest conditions like metabolic acidosis, kidney disease, or diabetes. Interpretation should be done alongside other tests and clinical evaluation by a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring of albumin concentration may be necessary for certain medical conditions.
What conditions or diseases can cause abnormal results in an anion gap blood test?
Abnormal anion gap results in a blood test can be indicative of various conditions or diseases. These may include diabetes, kidney disease, liver disease, certain medications, and toxins. Consultation with a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the underlying cause of abnormal anion gap levels.
Is fasting necessary before taking this blood test?
Fasting is not required for the Anion Gap blood test. However, it's advisable to avoid food and drink, except water, a few hours before the test. Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you're taking, as they may impact the test results. The test measures electrolyte levels and aids in diagnosing metabolic acidosis.
Can medications or supplements affect the results of an anion gap blood test?
Certain medications and supplements have the potential to affect the results of an anion gap blood test. It is important to inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking before undergoing the test to ensure accurate results.
What is the normal pH level of blood?
The anion gap blood test measures the levels of different electrolytes in the blood, including bicarbonate, sodium, and chloride. One important aspect of this test is to determine the pH level of the blood. The normal pH range for blood is between 7.35 and 7.45, which is crucial for maintaining proper pH balance. If the pH level falls below this range, it can indicate acidosis, a condition where there is too little acid in the blood. Conversely, if the pH level rises above this range, it can indicate alkalosis, a condition where there is too much base in the blood. Monitoring the pH level through the anion gap blood test can help diagnose and manage these conditions, and in some cases, your doctor may order additional testing to ensure an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
What are hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis?
Hyperkalemia is a condition characterized by elevated levels of potassium in the blood, while metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces excessive acid or loses too much bicarbonate in urine. The anion gap blood test can help diagnose these conditions in critically ill patients, and treatment may involve medication, dietary changes, or other interventions based on the underlying cause. Certain poisons, such as methanol (wood alcohol), too much aspirin, or antifreeze, can also cause acidosis, as well as proximal renal tubular acidosis, a condition where the kidneys do not take in enough bicarbonate and it is lost in urine.
How can doctors use the results of an anion gap blood test to diagnose and treat medical conditions?
Doctors can utilize the results of an anion gap blood test to diagnose and treat life-threatening metabolic acidosis, a condition characterized by excessive acid in the blood. Treatment for metabolic acidosis may involve medications or lifestyle changes, depending on the underlying cause. If diabetes is the cause of the condition, regular monitoring of anion gap levels aids in tracking treatment effectiveness, including the use of insulin to manage blood sugar levels. Additionally, anion gap levels can aid in the diagnosis and treatment of salicylate poisoning, a condition brought on by a salicylate overdose that can be fatal if not treated right away.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the anion gap blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool that helps healthcare professionals assess the balance of electrolytes in your body. By measuring the levels of positively and negatively charged ions, this test provides insights into various health conditions and helps guide treatment decisions. It is important to follow the necessary preparations before taking the test and communicate any medications or supplements you may be taking. Your healthcare provider will analyze the test results after you have taken them to look for any abnormalities or imbalances. If you are interested in purchasing the anion gap blood test at a discounted price, visit DiscountedLabs.com for more information. Remember, regular monitoring of your electrolyte levels can help ensure optimal health and well-being.
Buy a CMP test on DiscountedLabs.com
Citations:
[2] What to Know About the Anion Gap Blood Test