Master Your D Vitamin Level: Health Optimization Guide
Key Highlights
- Vitamin D is important for your overall health. It helps with bone health, the immune system, and more.
- Many people lack enough vitamin D. This can cause problems like fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, and other health issues.
- You can get vitamin D from sun exposure, your diet, and supplements.
- It's easy to find out your vitamin D level with a blood test. If you have a deficiency, taking supplements can help.
- You can keep your vitamin D levels healthy by making informed choices and taking action.
Introduction
Vitamin D is very important for staying healthy. It helps with strong bones, a good immune system, and other important body functions, including preventing bone loss. Our bodies can make vitamin D when we get sunlight. However, there are many reasons why we might not get enough. Knowing your vitamin D level and working to improve it can really help your overall health, reducing the increased risk of weak bones, osteoporosis, and other health issues.
Understanding Vitamin D and Its Importance
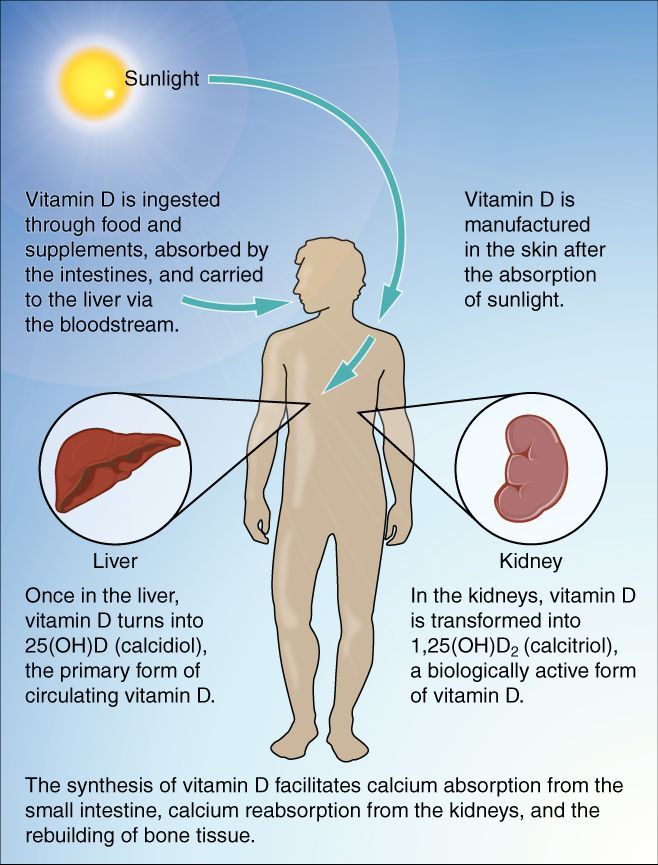
Vitamin D is special. It is different from other vitamins that we mostly get from food. Vitamin D works more like a hormone. Our skin produces it when we are in the sun. This vitamin is important for calcium absorption, which helps keep our bones and teeth strong.
But vitamin D does more than just help our bones. It also supports a healthy immune system, helps cells grow correctly, and plays a role in muscle function. This shows why having enough vitamin D is important for overall health and well-being.
The Role of Vitamin D in the Body
Vitamin D is important because it helps control calcium levels. These levels are key to bone health. Vitamin D allows the intestines to take in calcium from food. This keeps enough calcium in the blood for strong bones.
Also, vitamin D helps keep a good balance of calcium and phosphorus. Both are needed to make and keep bones healthy. This balance helps stop diseases like osteoporosis, which makes bones weak and fragile.
Besides helping bones, vitamin D is also good for the immune system. It affects how immune cells work, helping the body fight off infections and stay strong against germs.
How Vitamin D Affects Overall Health
Vitamin D is often linked to bone health, but it also plays a big role in overall health. Muscle weakness can be a sign of low vitamin D levels. This shows how important vitamin D is for muscle function and strength.
Research shows that having low vitamin D can lead to a higher risk of chronic diseases. These diseases include heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. While more studies are needed to prove these links, keeping up your vitamin D levels is a good idea for better health.
Additionally, enough vitamin D can help with mood and brain function. Some studies suggest that it may provide benefits for people who feel depressed. However, more research is still needed to support these claims.
Identifying Vitamin D Deficiency
Recognizing vitamin D deficiency can be hard. The symptoms often appear slowly and can feel like other health issues. However, if you have ongoing fatigue, muscle weakness, body aches, or bone pain, especially in your lower back, it might mean you need more vitamin D.
You should see your doctor if you notice these signs or have risk factors. These risk factors include not getting enough sun, having darker skin, or having digestive problems that make it hard to absorb vitamins. A simple blood test can check your vitamin D status.
Low Vitamin D Levels: Common Signs and Symptoms of Insufficiency
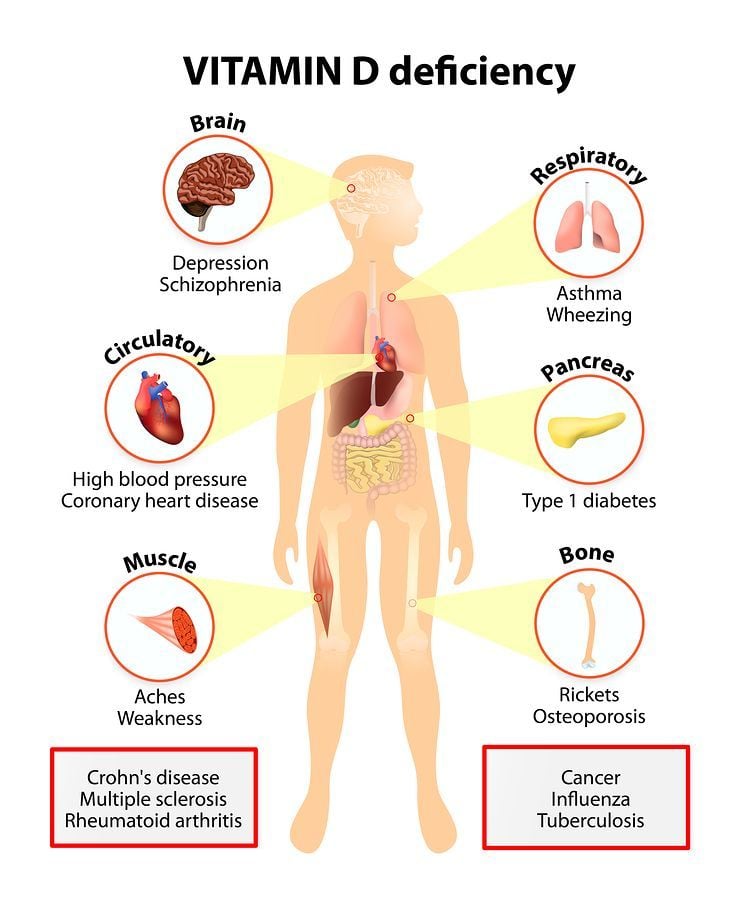
Severe vitamin D deficiency can cause serious issues. It may lead to rickets in children, which means their bones become soft and weak. In adults, it can cause osteomalacia, with similar bone problems. Milder cases often show less clear signs. Common issues include tiredness and low energy, even if you get enough sleep. Additionally, a lack of vitamin D can lead to muscle weakness and bone pain, and in children, it may cause incorrect growth patterns and deformities in joints. Understanding the common signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, such as fatigue, frequent illness, anxiety, bone pain, and slower wound healing, is crucial in optimizing your vitamin D level for better health. Treatments may include dietary changes or taking supplements.
You might also feel muscle weakness or cramps. These can happen because vitamin D helps your muscles work and recover. If you have trouble climbing stairs or feel weaker than usual, it could be a sign of vitamin D insufficiency.
Bone pain can be another warning sign. This pain often feels dull and achy, mainly in the lower back, hips, and legs. If you have ongoing bone pain along with other symptoms, it's a good idea to see your doctor. They can check your vitamin D levels.
Risk Factors for Vitamin D Deficiency
Certain factors can raise the chance of vitamin D deficiency. It is important to understand your own situation. For example, people with darker skin have more melanin. This can lower the amount of vitamin D made from sun exposure.
Also, individuals with specific medical conditions, like celiac disease, Crohn's disease, or cystic fibrosis, face a higher risk. Their bodies may find it hard to absorb enough vitamin D, even if they get enough or spend time in the sun.
Other risk factors for vitamin D deficiency include being older, as the body makes less vitamin D from sunlight over time. People with obesity may also be affected since fat cells can hold onto vitamin D. Limited sun exposure can also be a problem, especially for those who live in areas with less sunlight or have a lifestyle that limits time spent outdoors. Additionally, the use of sunscreen, while important for preventing skin cancer, can also block vitamin D production and absorption of vitamin D from the digestive tract. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, these factors can increase the risk of developing vitamin D deficiency.
Assessing Your Vitamin D Levels
Determining your vitamin D status is easy. It requires a simple blood test that checks the amount of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in your blood. This test gives you important information about your body's vitamin D levels.
If your levels are below the normal range, your healthcare provider can suggest ways to increase them. This usually means adding vitamin D supplementation to your routine. Doing this will help you correct the deficiency and keep your vitamin D at healthy levels.
When to Consider a Vitamin D Test
A vitamin D blood test is not usually part of regular health check-ups. However, you should get one if you have symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, or frequent infections. This test can show if low vitamin D is affecting your health.
If you have risk factors for low vitamin D, such as limited sun exposure, having darker skin, or disorders that affect absorption, you should talk to your doctor about testing. Some medications can also interfere with how your body takes in vitamin D.
It can be a good idea for older adults, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and people with conditions like osteoporosis or chronic kidney disease to check their vitamin D levels regularly. They may need more vitamin D to stay healthy.
Understanding Your Test Results
Interpreting your vitamin D test results means understanding the units used and what is considered a normal range. Vitamin D levels are usually measured in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). While the ideal range can change a little depending on the lab, a level of 20 ng/mL or higher is usually seen as enough for most healthy adults.
If your levels are between 12-20 ng/mL, this may mean you have vitamin D insufficiency. This can raise the risk of health problems. In these cases, your healthcare provider might recommend changes to your diet, more sun exposure, or vitamin D supplementation to get your levels back to normal.
Levels lower than 12 ng/mL are considered deficient, putting you at high risk for vitamin D deficiency. This often requires vitamin D supplementation to fix the deficiency. Your healthcare provider will decide the right dose and how long you need to take the supplements. They will base this on your needs, any medical conditions, and follow up with blood tests to check your progress and determine your level of vitamin d. Understanding your test results and maintaining a healthy level of vitamin d is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Sources of Vitamin D
Our bodies get vitamin D from three main sources: sunlight, food, and supplements. Sunlight is the best way to raise vitamin D levels naturally. But it’s important to be safe in the sun to lower the risk of skin cancer.
There are some foods that provide vitamin D. These include fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, as well as egg yolks. Fortified foods like milk, yogurt, and breakfast cereals also contain vitamin D. If you do not get enough vitamin D from food or sunlight, supplements can help.
Sunshine, Diet, and Supplements
Sunshine is the best way to boost your vitamin D levels naturally. When UVB rays from the sun touch our skin, they help change a type of cholesterol into vitamin D3. Usually, spending just 10-15 minutes in the midday sun, several times a week, with some skin exposed (without sunscreen), is enough to make a good amount of vitamin D. However, things like the time of day, the season, where you live, your skin color, and if you use sunscreen can affect how much vitamin D you produce.
Some foods can also help, even if they don’t give as much vitamin D as sunlight. Fatty fish, like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines, are great sources of vitamin D. Egg yolks also have some vitamin D and can help with your overall intake.
If you can't get enough from your diet or the sun, dietary supplements can help you reach better vitamin D levels. There are two types of supplements: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). D3 is frequently better because the body can absorb and use it more readily.
Safe Sun Exposure Practices
While sun exposure is crucial for vitamin D production, practicing safe sun exposure habits is paramount to minimizing skin cancer risks. Always prioritize sunscreen use, especially during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), to protect your skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during midday, and seek shade when possible. Covering up with protective clothing, including wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts and pants, offers additional protection from the sun's rays.
Here's a quick guide for safe sun exposure:
|
Factor |
Recommendation |
|
Time of Day |
Before 10 a.m. or after 4 p.m. |
|
Duration |
10-15 minutes of exposure, several times a week |
|
Skin Exposure |
Expose arms, legs, or back |
|
Sunscreen |
Use SPF 30 or higher, even on cloudy days |
Optimizing Vitamin D Intake
Getting enough vitamin D is important, and there are several ways to do it. You can start by adding vitamin D-rich foods to your diet.
Getting safe sun exposure is also important. If you can't get enough from food or sunlight, then vitamin D supplements can help. It's a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider about the right amount to take to optimize your intake of the sunshine vitamin. This is important to prevent any problems that can come from taking too much.
Recommended Dietary Sources
Eating foods that are high in vitamin D can help you reach and keep good levels of this vitamin. Include fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines in your meals. These fish are great sources of vitamin D.
Dairy products can help too since they are often added with vitamin D. Milk, yogurt, and cheese can help you get what you need daily. Try to pick fortified dairy products to boost your vitamin D levels.
Don't forget about a fortified breakfast. Many breakfast cereals come with added vitamin D, making them an easy choice. You can make your breakfast even better by adding fortified milk and some sliced fruits. This will give you a healthy start to your day with lots of vitamin D.
Choosing the Right Vitamin D Supplement
Navigating vitamin D supplements can be confusing. You need to know about dosages and the different forms. These supplements show their strength in International Units, or IU.
When choosing a supplement, pick vitamin D3 (called cholecalciferol). This form works better in the body than vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol). Dosage can change based on your personal needs and how severe any deficiency is.
It's best to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help find the right dose for you. Most adults need about 600-800 IU each day. Older adults might need higher doses. Your healthcare provider will give you recommendations that fit your health and blood test results.
The Impact of Vitamin D on Health Conditions
Maintaining good vitamin D levels is very important for our health. It helps our bodies absorb calcium and keeps our bones healthy. This is key in preventing osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition that makes bones weaker and raises the risk of fractures.
Research also shows that vitamin D may help our immune system. This could affect how we handle infections, autoimmune diseases, and some types of cancer. While we need more studies to confirm direct links, keeping up with vitamin D levels is widely seen as good for overall health and for preventing disease. In fact, observational studies and clinical trials have shown mixed evidence of the impact of low levels of vitamin D on various health conditions.
Bone Health and Osteoporosis Prevention
Vitamin D is an important nutrient for keeping our bones healthy throughout life. It helps our bodies absorb calcium, which is essential for strong bones. When our vitamin D levels are good, our body can effectively take calcium from food. This calcium is necessary for healthy bone growth and upkeep.
Vitamin D also helps increase bone mineral density, which is a way to measure how strong our bones are. Research shows that higher levels of vitamin D can lower the chance of getting osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become weak and are more likely to break.
In addition, vitamin D works well with other nutrients like calcium and phosphorus. Together, they help maintain bone remodeling. This process involves breaking down old bone and forming new bone. Keeping this balance ensures that our skeletons stay strong as we get older.
Vitamin D's Role in Immune Function
Emerging research shows that vitamin D plays many roles in how our immune system works. It helps our body fight infections and may affect how likely we are to get autoimmune diseases. Vitamin D receptors are present on different immune cells. This suggests that vitamin D directly influences how our immune responses work.
Studies indicate that vitamin D might boost the activity of white blood cells. These cells are important for fighting infections. It may also help control the production of cytokines. Cytokines are signals that help manage immune responses and keep inflammation under control.
As research continues to explore the link between vitamin D and the immune system, keeping enough vitamin D in our bodies is seen as helpful for our immunity. It might also lower the risk of autoimmune diseases, which happen when the immune system wrongly attacks our own tissues.
Overcoming Vitamin D Deficiency
Overcoming vitamin D deficiency requires a few steps. You can change your diet, get sensible sun exposure, and, if needed, take supplements. Eating foods that are high in vitamin D, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified products, can help increase your intake.
Also, getting safe sun exposure allows your skin to make vitamin D naturally, which can raise your levels. If changing your diet and getting sun don't work, vitamin D supplements can help. It is important to do this with the guidance of your healthcare provider to keep your vitamin D levels where they should be.
Strategies for Increasing Vitamin D Levels
Embracing a complete way to boost vitamin D levels can give you lasting results. First, add foods rich in vitamin D to your meals. Include fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel at least twice a week. You can also eat egg yolks, which are a good source of vitamin D, as well as other food sources such as fortified dairy products. Choose dairy products that are fortified with vitamin D and check out the many vitamin D-fortified options available at most stores. Additionally, spending time in direct sunlight can help your body convert a chemical in your skin into the active form of vitamin D, known as calciferol.
Next, focus on safe sunlight exposure. Let your skin catch some sun without sunscreen for short periods; this can greatly help with vitamin D production. Try to get 10-15 minutes of sun on your arms and legs a few times weekly during gentle hours, either before 10 a.m. or after 4 p.m.
If changing your diet and getting sun is not enough for your vitamin D needs, or if you have medical conditions that affect how your body absorbs it, consider vitamin D supplementation. This may be especially important for those who have undergone weight-loss surgeries such as gastric bypass surgery, which can make it difficult for the body to absorb sufficient quantities of certain nutrients. Talk with your healthcare provider to find the right dosage and method of supplementation for you and your health history. The National Institutes of Health recommends consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation regimen.
Monitoring Your Progress
Once you start using ways to raise your vitamin D levels, it’s important to track your progress with regular blood tests. This shows how well your method is working and helps your doctor make any needed changes.
Follow-up blood tests are usually done a few months after you start taking vitamin D supplements or change your diet or lifestyle. These tests give important information about how your body is responding to the changes and if your vitamin D levels are in the right range.
Your doctor might suggest changing your supplement dose, improving your diet, or altering your sun exposure habits based on your blood test results. Regular checking helps ensure you are moving in the right direction to reach and keep healthy vitamin D levels for good health and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, keeping your vitamin D level healthy is important for your overall health and well-being. It’s key to know why vitamin D matters, how to spot a deficiency, and how to check and increase your levels to stay healthy. You can get vitamin D from sunlight, food, or supplements. Getting enough vitamin D can help improve your bone health and support your immune system. By watching your levels and making changes when needed, you can help your body work at its best and avoid deficiencies. Make your health a priority by learning more and taking steps to boost your vitamin D levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I need a Vitamin D test?
If you have signs of low vitamin D, have risk factors for it, or worry about your vitamin D level, talk to your healthcare provider. They can check your needs and let you know if you need a blood test.
Can too much Vitamin D be harmful?
Yes, taking too much vitamin D, especially from high-dose supplements, can cause vitamin D toxicity. This leads to high calcium levels in the blood, which can result in different side effects. It is important to talk to your doctor to find out a safe limit for how much you can take.
How often should I check my Vitamin D levels?
The frequency of checking your vitamin D levels depends on personal factors. Your doctor can suggest how often you should be tested based on your risk factors, your vitamin D status, and your overall health.
Sources
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23168298/





