Thyroid Tests and What They Mean: Thyroid Test Results Chart
Decoding Thyroid Test Results Chart: What They Mean
The Challenge of Diagnosing Thyroid Dysfunction
One may assume that diagnosing thyroid-related conditions is straightforward, given the broad range of symptoms and potential impact on multiple organ systems. However, even with readily available blood tests for thyroid, pituitary, liver, and adrenal function, diagnoses are frequently missed.
The Misconceptions Surrounding TSH Levels and Hypothyroidism Diagnosis
One widespread misconception is the overreliance on increased Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels as a definitive indication of hypothyroidism. In response to low levels of thyroid hormone circulating in the blood, the pituitary gland releases this hormone. An increased TSH level can certainly confirm hypothyroidism, but it can also indicate an overactive thyroid gland, commonly associated with an overactive thyroid gland, making it an overly simplistic measure that overlooks many individuals with the condition.
There is a growing belief that the current accepted range of TSH levels from 1.0–4.5 is too broad, suggesting a more appropriate range of TSH levels would be 0.5–1.5. With this adjusted range, more patients could potentially receive a hypothyroidism diagnosis, aligning with a more accurate range of TSH levels.
Moreover, TSH levels measured in the lab can vary throughout the day, making them less reliable as an average measure. Factors like monosodium glutamate (MSG) and stress can lower TSH levels, further complicating its reliability as a diagnostic tool, which in turn can impact brain development in individuals, particularly during critical growth periods, and significantly affect overall brain development.
Understanding Thyroid Function and Its Importance
The thyroid gland plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health through the production of thyroid hormones, primarily T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine). These hormones regulate essential bodily functions including metabolism, energy levels, and even mood stability. When the thyroid gland functions optimally, it ensures that the body's metabolic processes are aligned, helping to maintain weight, energy balance, and mental clarity. A dysfunction in thyroid function can lead to a cascade of health issues, such as fatigue, weight gain or loss, and cognitive disturbances, highlighting the importance of keeping this small but powerful gland healthy for overall health and well-being.
In addition to its metabolic functions, the thyroid gland influences heart rate, body temperature, and menstrual cycles, demonstrating its integral role in multiple physiological systems. An imbalance in thyroid hormone levels can disrupt these systems, leading to conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, and can also significantly affect heart rate. Therefore, understanding thyroid function is crucial not only for diagnosing thyroid-related disorders but also for comprehending how they can impact overall health, heart rate, and quality of life.
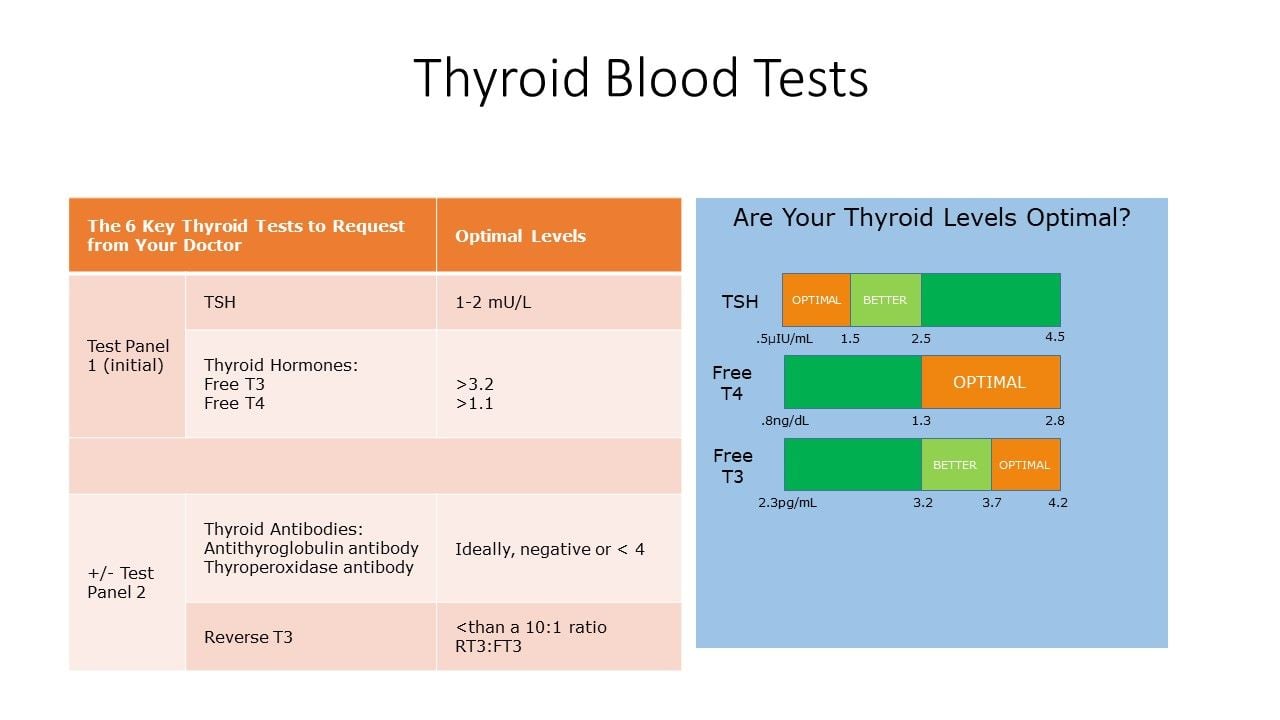
How to interpret the thyroid test results chart?
Interpreting thyroid test results involves looking at levels of thyroid hormones like TSH, T3, and T4. Abnormal results may indicate hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Consult your healthcare provider for a thorough analysis and appropriate treatment if needed.

TSH Levels Chart
Category | TSH Levels (mU/L) | Indication | Symptoms
Normal TSH Levels | 0.4-4.5 | Normal thyroid function | None
Optimal Range (Younger Adults) | 0.45-2.5 | Normal thyroid function | None
Pregnancy
- First Trimester | 0.1-2.5 | Normal for pregnancy | Thyroid medication adjustments may be necessary if your thyroid medication levels are outside this range.
- First Trimester | 0.1-2.5 | Normal for pregnancy | None
- Second Trimester | 0.2-3.0 | Normal for pregnancy | None
- Third Trimester | 0.3-3.0 | Normal for pregnancy | None
High TSH Levels | >4.5 | Hypothyroidism | Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, depression, dry skin
-
Subclinical Hypothyroidism | 4.7-10 | Mild hypothyroidism in pregnant women | May be asymptomatic or exhibit mild symptoms | Important to monitor during early pregnancy for pregnant women
- Symptomatic Hypothyroidism | >10 | Severe hypothyroidism | More pronounced symptoms
Low TSH Levels | <0.4 | Hyperthyroidism | Rapid heartbeat, weight loss, nervousness, tremors, increased sweating
- Subclinical Hyperthyroidism | 0.1-0.5 | Mild hyperthyroidism | May be asymptomatic or mild symptoms
- Symptomatic Hyperthyroidism | <0.1 | Severe hyperthyroidism | More pronounced symptoms
TSH Levels by Age and Gender
Age Group | Men (mU/L) | Women (mU/L)
18-30 years | 0.5-4.15 | 0.4-2.34
31-50 years | 0.5-4.15 | 0.4-4.0
51-70 years | 0.5-4.59 | 0.46-4.68
71-90 years | 0.4-5.49 | Not specified
TSH Levels in Children
Age Group | TSH Levels (mU/L)
0-4 days | 1.6-24.3
2-20 weeks | 0.58-5.57
20 weeks – 18 years | 0.55-5.31
This table provides a clear and concise overview of TSH levels, their implications, and associated symptoms. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized medical advice and treatment.

Evaluating Thyroid Hormone Levels: T4, T3, and FTI
Unreliability of Traditional Thyroid Hormone Tests
Traditionally, the levels of thyroid hormones are measured using tests for Total T4 (T4), T3-Uptake, Free Thyroxine Index (FTI or T7), and Total T3 (T3-by-RIA). However, these tests may not provide accurate reflections of functional hormone levels because they don't measure the thyroid levels of the hormone that are actually available for action.
Only free T4 and free T3 are available to act on the cells. However, typical tests measure a mixture of protein-bound T4 and T3 (which are unavailable to cells) and free T4 and T3. Therefore, a significant number of individuals may have abnormally low levels of free T4 and T3, even when traditional tests indicate normal results.
Broadening the Diagnostic Tools: Beyond Standard Thyroid Tests
While traditional thyroid blood tests, such as TSH, T4, and T3, provide valuable insights into thyroid function, they are often insufficient for a comprehensive evaluation of thyroid health. A broader spectrum of diagnostic tools, including a thyroid panel, can enhance the accuracy of thyroid assessments. For instance, advanced thyroid panel tests that measure both free T4 and free T3 levels can give a clearer picture of hormone availability for metabolic processes. This can be particularly beneficial in cases where patients present symptoms of thyroid dysfunction despite normal TSH levels.
Additionally, imaging techniques such as thyroid ultrasound can be instrumental in identifying structural abnormalities within the gland, including nodules or inflammation. These tests, including thyroid ultrasound, when combined with clinical evaluations, offer a more holistic approach to understanding thyroid health. By integrating these broader diagnostic tools, healthcare providers can more accurately assess thyroid conditions and tailor appropriate treatment plans, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Other Kinds of Thyroid Function Tests
Traditional thyroid hormone tests may not always provide a comprehensive view of thyroid function, particularly in cases of an underactive thyroid condition. Factors such as stress, illness, or medication can influence results, leading to potential misinterpretation. Newer diagnostic tools offer a broader perspective, including tests like thyroid ultrasound or thyroid peroxidase antibodies. These advanced tests help identify underlying causes of thyroid dysfunction beyond what standard tests reveal, guiding healthcare providers towards more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. Integrating these innovative tools can significantly enhance the accuracy of thyroid disorder management.
The Need for a More Holistic Approach to Diagnosis
Evaluating Symptom Improvement through Treatment
Complicating matters further, symptoms of hypothyroidism and thyroid dysfunction can emerge even with normal blood test results. When treated for hypothyroidism, patients with low free T4 and free T3 levels—regardless of TSH levels—often report significant improvement. Symptoms of hypothyroidism may also vary among individuals, making diagnosis more challenging.
Some patients exhibit symptoms of low thyroid action, even when their test results suggest otherwise. As a result, many skilled thyroidologists consider a patient's response to treatment as the primary determinant of a hypothyroidism diagnosis. If symptoms improve with appropriate treatment, it provides compelling evidence of hypothyroidism. Several reputable introductory textbooks strongly support this method of diagnosis.
Symptoms and Causes of Thyroid Dysfunction
Thyroid dysfunction can manifest through various symptoms, including unexplained weight changes, fatigue, and mood swings. Other signs may involve hair loss, intolerance to cold or heat, and irregular menstrual cycles in women. The causes of thyroid dysfunction are diverse and can include autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, or thyroid cancer. Understanding these symptoms and causes, particularly Hashimoto's thyroiditis, is crucial for early detection and effective management of thyroid disorders.

Symptoms of High and Low TSH Levels
Understanding the symptoms associated with high and low TSH levels is crucial for recognizing thyroid dysfunction. High TSH levels typically indicate hypothyroidism, where the body experiences fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and depression, among other symptoms. Patients may also notice dry skin and hair, constipation, and a general decrease in energy levels. On the other hand, low TSH levels are indicative of an overactive thyroid gland, or hyperthyroidism, leading to symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, unintended weight loss, increased sweating, and anxiety. Individuals may feel nervous or shaky and experience changes in their menstrual cycles. It is important to recognize that these symptoms can significantly impact quality of life and may vary from person to person, emphasizing the need for thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Interpreting the Results: What Your Thyroid Test Numbers Really Mean
Interpreting thyroid blood tests results can often feel daunting, especially when faced with a range of numbers that may not clearly indicate a health issue. The key to understanding your thyroid blood test results lies in recognizing the significance of each hormone measured. Thyroid blood tests TSH levels serve as an initial screening tool; a high TSH often suggests hypothyroidism, while a low TSH may indicate hyperthyroidism. However, TSH alone does not provide a complete picture. Free T4 and Free T3 levels must also be considered to gauge the active hormone available for the body's metabolic needs.
Moreover, it is vital to understand that these values can fluctuate based on various factors, including age, gender, and even the time of day the test was conducted. Therefore, a single test result should not be taken in isolation. Instead, it's essential to discuss these numbers with a healthcare provider who can interpret them in the context of your overall health, symptoms, and any existing medical conditions. A thorough understanding of your thyroid test results can empower you to take informed steps toward managing your thyroid health effectively.
Next Steps Following a Thyroid Diagnosis
After receiving a thyroid diagnosis, the next steps typically involve discussing treatment options with your healthcare provider. This may include thyroid hormone replacement therapy, medication adjustments, or lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring of thyroid levels, including crucial thyroid levels and hormone levels through follow-up blood tests, is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will work closely with you to manage your condition and address any concerns or symptoms that may arise. Maintaining open communication and adhering to the recommended follow-up schedule are key in managing thyroid health effectively.
Understanding Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism Treatments
When dealing with hypothyroidism, the mainstay of treatment is thyroid hormone replacement therapy (THRT), commonly administered as levothyroxine. This synthetic form of the thyroid hormone T4 helps restore normal hormone levels, alleviating symptoms and preventing complications such as heart disease and weight gain. Patients typically require regular monitoring of TSH and T4 levels to fine-tune their medication dosage. Conversely, hyperthyroidism treatments may involve anti-thyroid medications like methimazole, which help reduce the production of thyroid hormones. In some cases, radioactive iodine treatment or surgical intervention may be necessary to control hormone levels effectively. Both conditions necessitate a personalized approach, taking into account individual health status and symptom severity to guide treatment decisions.
Conclusion
Thyroid dysfunction, particularly hypothyroidism, can manifest in a myriad of ways and impact numerous organ systems. While diagnostic tests are readily available, their sensitivity and specificity often fall short, leading to missed or incorrect diagnoses. Over-reliance on traditional thyroid tests can overshadow more nuanced indicators like free T4, free T3 levels, and symptoms of hyperthyroidism, which can include tremors and palpitations, as well as symptom improvement with appropriate treatment.
For a more comprehensive understanding of thyroid health, it's crucial to look beyond standard measures and consider the full range of symptoms and patient responses to treatment, especially if there is a significant family history of thyroid disease. This holistic approach not only ensures a more accurate diagnosis but also helps guide effective treatment strategies that can significantly improve patients' quality of life.
Take Action for Your Health
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to your health. Don't let misunderstood tests or overlooked symptoms stand between you and the right diagnosis. Take control of your thyroid health by getting comprehensive, affordable thyroid tests and panels at DiscountedLabs.com.
At Discounted Labs, we provide easy and affordable access to a wide range of tests, ensuring you get a complete picture of your thyroid health. It's time to move beyond the confusion and embrace a path towards better health and wellbeing. Visit DiscountedLabs.com and order your thyroid test today.
References
-
https://thancguide.org/2024/06/the-journey/how-to-decode-your-thyroid-function-tests-now/
-
https://www.verywellhealth.com/interpret-your-thyroid-test-results-3231840
-
https://www.verywellhealth.com/understanding-thyroid-blood-tests-low-or-high-tsh-3233198






