Understanding the CPK Lab Test: Importance and Factors

Mastering the CPK Test: Importance & Factors
A CPK lab test, also known as a creatine phosphokinase assessment, is an analysis that can give important information about the wellbeing of muscles and other tissues. This article offers a thorough explanation of the CPK blood test, its role in assessing the health of muscles and tissues, and its application in diagnosing muscular injuries or genetic disorders.
Throughout this post, we will explore the role of creatine phosphokinase in our bodies and how a CPK blood test works. We'll discuss various reasons for ordering a CPK blood test, such as diagnosing muscle injuries and genetic testing for muscular dystrophy. Furthermore, we'll compare troponin tests with CPK isoenzyme tests to identify specific tissues affected by damage.
As we proceed, we'll also debunk common misconceptions about elevated levels of creatine kinase due to exercise or other conditions. Lastly, you will learn about monitoring changes in enzyme levels over time and factors that can influence these levels, like race-related differences and gender-specific variations.
Understanding the CPK Test
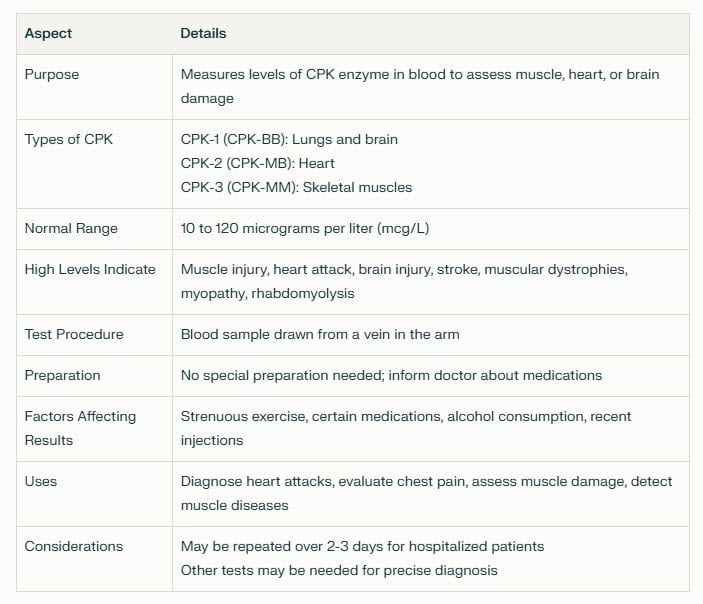
A CPK blood test, also known as a creatine phosphokinase (CPK) isoenzyme test, checks the levels of these enzymes in your blood. Your heart, brain, and skeletal muscles contain the important enzyme creatine phosphokinase, which causes specific chemical changes in your body. The amount of creatine kinase in your blood can indicate stress or injury to your heart or other muscles, with small amounts also found in the brain. High levels of CPK indicate a higher amount of creatine kinase in the blood, which can be a sign of muscle damage or disease. The main use of a CK test, also known as a creatine kinase test, is to diagnose and monitor injuries and diseases that damage skeletal muscles and cause high levels of CK in your blood. However, conditions that damage the heart muscle and the brain may also benefit from its use. Understanding CPK blood tests is crucial for identifying and managing these health concerns.
The Role of Creatine Phosphokinase in the Body
CPK helps create ATP, the energy source for muscle contractions, by converting creatine into adenosine triphosphate. When there's damage to muscle tissue, whether it's due to physical trauma or disease, the cells release higher amounts of CPK into the bloodstream.
How a CPK Blood Test Works
To perform a CPK blood test, healthcare professionals will draw a small sample of blood from a vein using a needle and syringe. Technicians then send the sample to a laboratory to measure the amount of creatine phosphokinase present during a specific test. Results are typically available within several days and can help your health care provider determine if further testing or treatment may be necessary based on elevated enzyme levels. The test involves collecting a small amount of blood into a test tube or vial, and the needle's entry or exit may cause a slight sting. This usually takes less than five minutes.
Note: Normal ranges for CPK levels vary depending on factors such as age, sex, race, and activity level; therefore, it's essential to consult with medical professionals when interpreting results.
Overall, CPK blood tests can provide valuable information about the health of your muscles and should be considered if you are experiencing any muscle-related issues. Be sure to understand the purpose and potential outcomes of a CPK test before taking it.
Reasons for Ordering a CPK Blood Test
Medical professionals can request a CPK test, also known as a creatine phosphokinase isoenzyme test, for a variety of reasons. We use multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to determine a person's genetic susceptibility to muscular dystrophy. Patients undergo ultrasonography to detect deletions in the dystrophin gene. Dystrophic patients should have electrocardiography and pulmonary function tests before surgery as part of their hematologic workup. If a patient exhibits symptoms like muscle pain, muscle weakness, or muscle cramps, the doctor may also order this test to rule out muscle-related issues.
Diagnosing Muscle Injuries
Elevated levels of CPK enzymes in a blood sample can indicate some sort of stress or damage to heart muscles, brain tissues, or skeletal muscles. Doctors can diagnose a number of conditions, such as myocardial infarction, rhabdomyolysis, and myositis, by checking the levels of CPK enzyme in the blood. This aids them in determining the appropriate treatment for the affected tissue type. This information helps guide treatment decisions based on the specific type of tissue affected.
Genetic Testing for Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of hereditary conditions characterized by the gradual weakening of muscles over time. Together with other diagnostic tools like PCR testing, a CPK lab test can determine whether an individual carries the gene responsible for certain types of muscular dystrophy. Early detection allows healthcare providers to implement appropriate interventions and provide guidance on managing symptoms throughout one's life.
When there are high levels of CPK in the blood, a CPK blood test can diagnose injuries or conditions that are already present. Regular health checks can also incorporate a CPK blood test to monitor overall health and detect issues before they escalate. By understanding the various reasons for ordering this type of blood test, individuals can better advocate for their own health and work closely with healthcare professionals to address any concerns.
The CPK blood test is an important tool for diagnosing muscle injuries and genetic testing for muscular dystrophy, allowing doctors to accurately identify the source of a patient's pain or discomfort. We can learn more about which specific tissues have experienced damage by contrasting troponin tests with CPK isozyme tests.
A CPK lab test can find muscle damage and problems, find people who are genetically more likely to get muscular dystrophy, check patients for deletions in the dystrophin gene, and check dystrophic patients before surgery. Elevated levels of CPK enzymes can indicate stress or damage to heart muscles, brain tissues, or skeletal muscles, and can be a crucial factor in evaluating chest pain. Early detection allows healthcare providers to implement appropriate interventions and provide guidance on managing symptoms throughout one's life.
Comparing Troponin Tests with CPK Isoenzymes Tests
A troponin test measures the levels of proteins called troponin T and troponin I in the blood. Troponin T and I are proteins that enter the bloodstream when cardiac muscle cells become injured, making them useful for diagnosing heart attacks or other related issues. On the other hand, a CPK isoenzyme test aids doctors in precisely identifying the damaged tissue when cells within skeletal or heart muscles undergo damage or degeneration, causing them to rupture and release large quantities into the bloodstream.
Advantages of Using Both Tests Together
- Better diagnostic accuracy: Combining both tests provides more accurate information about potential muscle damage and helps medical professionals differentiate between various causes of elevated enzyme levels.
- Multiple problems can be found: troponins only show damage to heart muscle, but CPK isoenzymes can also find damage in other tissues, which lets a full picture of health be made.
- Treatment guidance: The results from these tests can guide treatment decisions by providing insight into the severity and location of tissue damage.
Identifying Specific Tissues Affected by Damage
A CPK blood test's main advantage over a troponin test is its capacity to pinpoint the precise tissues that an injury has affected. There are three main types (isoenzymes) of creatine phosphokinase:
- CPK-MM, found primarily in skeletal muscles
- CPK-MB, found mainly in the heart muscle,
- CPK-BB, which is most commonly associated with brain tissue.
A high level of a certain CPK isoenzyme can help doctors figure out where the damaged tissue is coming from and whether the heart, brain, or muscles have been hurt. This information can be invaluable for determining appropriate treatment options and monitoring patient progress over time.
The comparison of troponin tests with CPK isoenzyme tests can provide valuable insight into the health of a patient. However, it is important to understand some common misconceptions about CPK blood tests in order to accurately interpret the results.
Common Misconceptions About CPK Blood Tests
When it comes to common misconceptions surrounding CPK blood tests, there are several factors worth noting. Contrary to popular belief, elevated CPK levels do not necessarily signify the presence of a muscle disorder. Contrary to popular belief, however, CPK levels may not always be indicative of a muscle disorder.
The Role of Exercise in CPK Levels
Studies have shown that intense physical activity and special preparation can cause temporary increases in CPK levels due to muscle breakdown and repair processes. This means that individuals who engage in regular exercise routines may experience higher-than-normal enzyme readings on their blood test results without necessarily having a muscle disorder or injury.
Other Conditions That Can Cause Elevated CPK Lab Test Results
- Seizures: Seizures can lead to increased muscle contractions and a subsequent elevation in creatine phosphokinase levels.
- Brain injuries: Traumatic brain injuries or strokes may result in damaged brain tissue, which could release high amounts of enzymes into the bloodstream.
- Infections: Certain viral infections, like influenza, can also cause temporary elevations in enzyme levels due to inflammation and damage inflicted upon muscles during infection.
- Certain medications: Some drugs, such as statins used for cholesterol management, have been known to cause an increase in CPK levels as a side effect (source).
In light of these potential causes for elevated creatine phosphokinase levels, it is crucial for medical professionals to consider a patient's overall health and lifestyle factors when interpreting CPK blood test results. A comprehensive evaluation may include additional diagnostic tests or follow-up assessments to accurately determine the underlying cause of any abnormal enzyme readings, including a thorough review of the processing of the test and further tests if necessary.
It is imperative to recall that CPK testing can be advantageous in diagnosing and tracking certain ailments, yet one must also be cognizant of the potential misinterpretations related to them. Monitoring changes in enzyme levels over time can provide valuable insights into how well treatments are working or if further testing may be necessary.
Monitoring Changes in Enzyme Levels Over Time
To monitor any changes in enzyme levels that could indicate damage or stress to the heart, brain, or skeletal muscles, such as kidney failure, medical professionals may repeat a CPK blood test, a simple blood test, over several days. This helps medical professionals assess overall health and wellness by providing insight into potential issues related to muscular injury or degeneration, specifically looking at the levels of total CPK in the blood.
Importance of Tracking Enzyme Level Trends
By tracking CPK levels, healthcare providers can gain valuable insight into potential muscular injuries or degeneration, thus allowing them to create treatment plans and interventions tailored to individual needs. For instance, a sudden increase in CPK levels might suggest an acute muscle injury, while consistently elevated levels could indicate chronic muscle inflammation or disease progression. By monitoring these trends, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding treatment plans and interventions tailored to individual needs.
How Doctors Use This Information for Treatment Decisions
The data obtained from a CPK test plays a crucial role in guiding doctors' treatment decisions. Depending on the underlying cause of elevated enzyme levels, different approaches may be taken:
- Muscle injuries: When doctors suspect muscle injuries due to high CPK values, they may recommend rest and physical therapy in addition to medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of muscular dystrophy if there are high levels of CPK enzymes. Treatments like corticosteroids can help slow the disease's progression, while rehabilitative exercises keep the person mobile.
- Rhabdomyolysis: Dark urine and severe muscle pain, along with an extremely high level of CPK, indicate rhabdomyolysis, a potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention, including intravenous fluids and medications to prevent kidney damage.
Ultimately, tracking CPK enzyme levels over time allows healthcare professionals to better understand a patient's unique situation and make the most appropriate treatment decisions for their specific needs.
Monitoring changes in enzyme concentrations over an extended period is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of treatments and potential health risks. Understanding factors that influence creatine phosphokinase levels is also essential for making informed decisions about one's health care needs.
Doctors use CPK lab tests to monitor changes in enzyme levels over time, which can provide valuable information about a patient's condition. By tracking trends and fluctuations, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding treatment plans tailored to individual needs, such as rest and physical therapy for muscle injuries or corticosteroids for muscular dystrophy.
Factors That Can Influence Creatine Phosphokinase Levels
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels can vary based on factors such as race, gender, and activity level. It is important to understand these differences in order to correctly interpret test results and figure out if a high reading could mean muscle inflammation due to disease progression, heart disease, or conditions that overlap rather than just a heart event.
Race-related Differences in Creatine Phosphokinase Levels
Different racial groups may have varying baseline levels of CPK enzymes. For example, studies have shown that African Americans tend to have higher average CPK levels compared to Caucasians. As this difference may affect diagnosis and treatment, it is important to consider when interpreting CPK blood test results.
Gender-specific Variations
Males generally exhibit higher creatine phosphokinase enzyme concentrations than females due to their larger muscle mass. As a result, normal reference ranges for males are typically higher than those for females. It's essential for healthcare providers to consider these gender-based differences when analyzing CPK blood test results.
The Impact of Physical Activity on CPK Test Levels
- Vigorous exercise: Intense workouts can cause temporary elevations in creatine phosphokinase enzyme concentrations because they stress muscles during exertion.
- Inactivity: Prolonged periods without physical activity may lead to lower-than-normal CPK values as muscles become less active over time.
- Sudden changes in exercise routine: A sudden increase or decrease in physical activity can also affect CPK levels, making it essential to consider a patient's exercise habits when interpreting test results.
By understanding the various factors that influence creatine phosphokinase levels, healthcare providers can more accurately interpret CPK test results and make informed decisions about their patients' health. This knowledge helps ensure that individuals receive appropriate care and treatment for any underlying conditions affecting their muscles or hearts.
Understanding the factors that influence creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels is crucial for the accurate interpretation of test results. When analyzing blood test results, factors like race, gender, and physical activity, particularly in a healthy adult, can influence CPK levels, necessitating appropriate care and treatment for any underlying conditions affecting the muscles or heart. In particular, physical activity can have a significant impact on CPK levels, as high levels of physical exertion can lead to muscle damage and an increase in CPK measurements. It is important to consider an individual's level of physical activity when interpreting CPK test results.
FAQs in Relation to Cpk Blood Test
What CPK level is considered high?
A CPK level above 200 U/L is generally considered high. However, normal values and ranges may vary depending on the laboratory and individual factors such as age, gender, and race. It's important to consult with your healthcare provider for a personalized interpretation of your results.
What causes extremely high CPK?
A lot of things, like muscle damage or injury, heart damage, intense exercise, a heart attack, muscular dystrophy, rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown), autoimmune myositis (inflammation), hypothyroidism, and some medications like statins, can cause CPK levels to be very high.
What are the symptoms of high CPK levels?
High CPK levels themselves do not cause symptoms; however, they may indicate an underlying condition causing muscle damage or inflammation. Symptoms associated with these conditions include muscle pain or weakness, fatigue, fever (in cases of infection or inflammation), and dark urine due to myoglobinuria in rhabdomyolysis cases.
Is CPK an inflammatory marker?
Muscles primarily contain the enzyme CPK, which is not an inflammatory marker itself. However, other tests like C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) are more specific markers for systemic inflammation. Check the inflammation panel on Discounted Labs.
Conclusion
Understanding CPK blood tests is important for anyone interested in maintaining their health and fitness. These tests can help diagnose muscle injuries, identify specific tissues affected by damage, and monitor changes in enzyme levels over time. It's also important to be aware of common misconceptions about CPK blood tests and factors that can influence creatine kinase levels.
If you're interested in getting a CPK blood test or other discounted lab panels, check out DiscountedLabs.com. DiscountedLabs.com provides access to low-cost testing options with simple results, enabling you to take charge of your wellbeing.
Click here to buy a CPK test on DiscountedLabs.com.
References:
CPK Test: High or Low Levels & What Results Mean
Creatine Phosphokinase Test - UCSF Health
Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) - Johns Hopkins Lupus Center
Creatine Phosphokinase Test - Mount Sinai Health System
What is CPK or CK Test and its Uses, Test Results, and Normal Range?
CPK Isoenzymes Test - UCSF Health
CPK Enzyme Test: What Do Your Results Mean? - WebMD
Creatine Kinase: MedlinePlus Medical Test
CPK Isoenzymes Test: Purpose, Procedure & Results - Healthline





