Vitamin D and Testosterone: Is There a Link?
Vitamin D and testosterone are two of the most important factors in our health but are often overlooked. This post will dive into the complex relationship between vitamin D and testosterone, looking at how deficiency affects our health and the results of The Graz Vitamin-D Randomized Clinical Trial on hormonal balance through a randomized controlled trial.
We’ll look at several studies that have investigated the correlation between 25(OH)D deficiency and sex hormones. And we’ll see how vitamin D supplementation can affect hormonal balance by looking at the results of The Graz Vitamin-D Randomized Clinical Trial.
We’ll also look at how much testosterone the testicular tissue can produce with different amounts of vitamin D and how blood levels of testosterone and vitamin D are related. And we’ll touch on symptoms of low testosterone and why it’s important to understand your Vitamin D status & hormonal balance for optimal health.
Introduction and Background on Vitamin D and Testosterone
Vitamin D and testosterone are two of the most important nutrients in our bodies and overall health. Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin that is important for bone health, immune function and reproductive health. It regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism so bones stay strong and healthy. Testosterone is a steroid hormone produced in the testes in men. It’s responsible for male characteristics like facial hair, deep voice and muscle mass.
Research shows a complex relationship between vitamin D and testosterone in men. Studies show that vitamin D deficiency is linked to low testosterone which can cause various health issues. Understanding this relationship is important for optimal health outcomes especially for men who are experiencing symptoms of low testosterone.
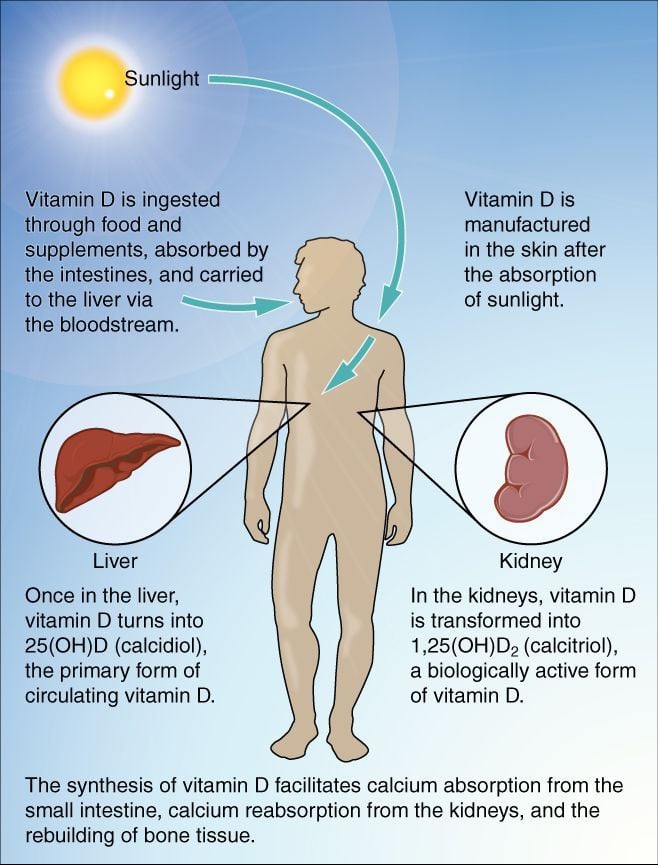
What is Vitamin D’s Role in the Body
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a big role in bone health, immune function and reproductive health. It regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism which are needed for strong bones and teeth. Vitamin D also supports the immune system to fight off infections and diseases.
We get vitamin D from sun exposure, diet and supplements. But many are deficient in vitamin D especially during winter when sun is scarce. Deficiency can cause various health problems like weak bones, increased susceptibility to infections and impaired immune function. Having adequate vitamin D levels is important for overall health and well-being.
Low Testosterone and Vitamin D Deficiency
Obesity is linked to low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) levels which in turn is associated with testosterone deficiency and low testosterone in young men. Hypovitaminosis of vitamin D can cause long term health problems like drop in testosterone production and higher risk of hypogonadism. In this section we’ll discuss what causes low testosterone and lack of vitamin D and how these two affects each other.
Causes of Low Testosterone and Vitamin D Deficiency
-
Poor diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients like vitamin-D rich foods such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products and egg yolks can cause deficiency. Those deficient in vitamin D may benefit from taking the right vitamin D supplement to address low testosterone.
-
Lack of sun exposure: Since our bodies synthesize vitamin D through sun exposure on our skin, not spending enough time outdoors or living at higher latitudes can cause deficiency.
-
Obesity: Excess body fat can disrupt hormone regulation and absorption/utilization of vitamins like vitamin D (source). This creates a vicious cycle where obesity causes low testosterone and worsen existing deficiency.
-
Aging: As men age, their natural ability to produce hormones like testosterone decreases. Older adults have lower 25(OH)D levels partly because they spend less time outdoors exposed to direct sunlight (source).
How Low Testosterone and Vitamin D Deficiency Affects Health
The interplay of low testosterone and vitamin D deficiency can cause:
-
Hypogonadism: A condition where the testes produce less or no hormones leading to symptoms like fatigue, decreased muscle mass and sexual dysfunction.
-
Osteoporosis: Both testosterone and vitamin D are important for bone density. Low levels of either nutrient can increase risk of osteoporosis (source).
-
Mood disorders: Studies show that there is a link between low testosterone/vitamin D deficiency and higher prevalence of depression and anxiety (source).
-
Cardiovascular disease: Research shows that men with lower levels of both hormones are at higher risk of cardiovascular events like heart attacks or strokes (source).
Given these health effects, it’s more important to know how obesity affects this interaction and how to balance our hormones as a whole.
Low testosterone and not enough vitamin D go together to create health problems so it’s clear there’s a strong connection between the two. We need to look into the studies on how vitamin D affects serum testosterone levels to understand more about these associations.
Summary: This article discusses the connection between low testosterone and vitamin D deficiency and their health effects. It’s clear that obesity plays a big role in the hormone relationship so understanding how these two work together is key to overall health.
Vitamin D and Testosterone Levels Research
In the recent years, many studies have been done to look into the relationship between vitamin D status and hormone balance especially on free bioavailable testosterone levels and testosterone production. Some studies show positive association between 25(OH)D levels and total/free testosterone levels while others found no significant relationship for certain hormonal parameters.
Studies on 25(OH)D deficiency and sex hormones
-
A study in Clinical Endocrinology (Oxf) found that men with sufficient vitamin D had higher total testosterone (TT), free testosterone (FT) and bioavailable testosterone compared to those with insufficient or deficient vitamin D. The researchers concluded that there is a strong relationship between 25(OH)D and TT/FT levels.
-
A study in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that low 25(OH)D was associated with hypogonadism in middle aged men but not with changes in luteinizing hormone (LH).
-
A more recent study in Andrology however found no significant correlation between 25(OH)D levels and various hormonal parameters like LH, FSH and inhibin B in healthy young men.
The studies show the complex relationship between vitamin D and testosterone production. We need to consider that age, ethnicity, BMI and overall health can affect 25(OH)D levels and hormonal balance in men.
A strong connection between 25(OH)D deficiency and sex hormones has been shown in Vitamin D and testosterone studies where testosterone levels were measured in nmol/L. We will now look into the effect of vitamin D supplementation on hormonal balance by examining the results of the Graz Vitamin D Randomized Clinical Trial.
Vitamin-D Supplementation and Hormonal Balance
One of the studies that looked into the relationship between vitamin D supplementation and hormonal balance is the Graz Vitamin-D Randomized Clinical Trial. The objective of this study was to compare the effects of taking vitamin D for 12 weeks to taking a placebo. The study showed significant differences between the vitamin D group and the placebo group in insulin resistance, hormone levels and other metabolic parameters. Some of the findings on how vitamin D affects testosterone and other metabolic parameters were quite interesting.
Graz Vitamin-D Randomized Clinical Trial Results
Improved Metabolic Parameters: Those who took vitamin D supplements had reduced insulin resistance which is key to overall health and preventing chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes.
Influence on Estradiol Levels: The supplemented group had increased estradiol levels which is one of the main female sex hormones. The supplemented group’s increase in estradiol levels was not statistically significant compared to the placebo group.
No Significant Effect on Total Testosterone (TT) Levels: Surprisingly, there was no difference in TT levels between those who took vitamin D supplements and those who did not. This means that while there may be a relationship between blood testosterone levels and vitamin D, supplementation may not have a significant impact on hormone production or regulation for everyone.
This study shows the complexity of hormonal balance in our body. Although it’s clear that getting the right nutrients like vitamin D is important for overall health, more research is needed to understand how they affect testosterone production. Those who want to optimize their hormone levels through diet or supplements should consult a healthcare professional and stay updated with the latest research.
The Graz Vitamin-D Randomized Clinical Trial results showed that taking vitamin D supplementation had a positive effect on hormonal balance. More research is needed to find out how hCG injections will affect men with different vitamin D levels and how there is a link between testosterone and vitamin D. More well-designed randomized controlled trials are needed to clarify these relationships.
Conclusion: So vitamin D supplementation may not affect testosterone levels but it seems to affect metabolic parameters and estradiol levels. More research is needed on how nutrients like vitamin D can alter or control hormone production so consult a specialist before starting any diet or supplementation program.
Testosterone and Vitamin-D
A study from Rigshospitalet found a relationship between testosterone, sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and vitamin D in 300 healthy men with normal testosterone production. This shows the importance of having adequate vitamin D for hormonal balance.
Vitamin-D and Testicular Tissue’s Ability to Produce Testosterone
Vitamin D is involved in many physiological processes including sex steroid production. In testicular tissue, it was found that low vitamin D can impair the ability to produce testosterone. Men with low vitamin D had less response to hCG injections compared to those with normal or high vitamin D levels. The studies included in this review were selected based on strict inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure the integrity and quality of the review process.
hCG Injections on Men With Different Vitamin-D Levels
-
Serum Levels: Those with higher 25(OH)D serum levels had increased total testosterone after hCG injections compared to those with lower 25(OH)D serum levels.
-
Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Response rate was also seen for luteinizing hormone which is responsible for stimulating testosterone production in the testicles.
-
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): No significant difference was seen in FSH response between the groups based on their initial 25(OH)D levels.
So there may be a link between testosterone and vitamin D but more research is needed to understand the implications. For overall health and wellness men should have healthy levels of both hormones.
Vitamin D is involved in testosterone production and regulation so let’s think about what this hormonal balance means to a person’s overall health.
Conclusion: The study showed a positive correlation between testosterone and vitamin D, higher 25(OH)D resulted to higher total testosterone, LH response was also better when 25(OH)D was normal or high. The study suggests there may be a link between the two which is important for men’s health.
Testosterone Production, Regulation and Health
Testosterone deficiency which has many health implications is produced in the testes and regulated by hormones like LH. It’s produced in the testicles and regulated by pituitary hormones like luteinizing hormone (LH). Low testosterone can have many negative effects on overall health. In this section we will discuss some of the common symptoms of low testosterone and why we need to understand Vitamin D status & hormonal balance.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
-
Fatigue: One of the most obvious symptoms of low testosterone is fatigue or lack of energy. Men may find it hard to be active or finish their daily tasks due to low energy.
-
Muscle loss: Testosterone is involved in muscle mass so deficiency leads to loss of muscle strength and size.
-
Low libido: Decrease in libido or sex drive often accompanies low testosterone. This may also result to erectile dysfunction in men.
-
Bone problems: Testosterone regulates bone density so deficiency can increase risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
-
Mood changes: Men with low testosterone may experience mood swings, irritability, depression or anxiety as their hormonal balance gets disrupted. li>
Why We Need To Understand Vitamin-D Status & Hormonal Balance
Vitamin D affects many physiological processes in our body including sex hormones like testosterone. As mentioned earlier studies showed a link between blood testosterone and vitamin D in healthy men with normal testosterone production. So maintaining optimal vitamin D levels may be important for hormonal balance.
But more research is needed to understand how these two work together in the body’s endocrine system. In the meantime men who are experiencing symptoms of low testosterone should consult their doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment that can improve both hormone levels and overall health.
Conclusion: This article discusses the link between Vitamin D and testosterone, the implications for men who are experiencing low energy or muscle loss. It discusses the common symptoms of low testosterone like low energy and muscle loss, bone problems and mood changes. And how maintaining optimal vitamin D levels can help preserve hormonal balance in men experiencing these symptoms.
Vitamin D and Testosterone in Women
Vitamin D and testosterone are often linked to men’s health but they also play a big role in women’s health. Vitamin D is important for bone health and immune function in women. It is also involved in the regulation of reproductive hormones for proper menstrual cycles and fertility. Testosterone although present in smaller amounts in women is involved in the development of female characteristics like libido and muscle mass.
Having adequate levels of both vitamin D and testosterone is important for women’s overall health. Vitamin D deficiency can cause many health problems like osteoporosis, autoimmune diseases and certain cancers. Low testosterone can affect libido, muscle mass and overall energy. Understanding the roles of these nutrients in women’s health is important to prevent and manage these conditions.
Why Vitamin D is important for Women’s Health
Vitamin D is important for bone health and immune function in women. It regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism so bones are strong and healthy. It also supports the immune system to fight off infections and diseases. It is also involved in the regulation of reproductive hormones for proper menstrual cycles and fertility.
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to many health problems in women like osteoporosis, autoimmune diseases and certain cancers. Having adequate vitamin D is important to prevent these conditions and overall health. Women should get enough vitamin D through sunlight, dietary sources and supplements if needed. Regular check-ups and blood tests can monitor vitamin D levels and ensure optimal health.
FAQs about Vitamin D and Testosterone
Does vitamin D increase testosterone?
There is some evidence that vitamin D may have a positive effect on testosterone. Studies show that taking vitamin D supplements can increase testosterone especially in men who are deficient. But more studies are needed to determine the ideal dosage and if other factors affect this relationship. To get the most out of vitamin D supplements for testosterone, you should also change your lifestyle like exercise more and eat better.
How much vitamin D for testosterone?
Vitamin D is important for testosterone production. Studies show that men with higher vitamin D levels have higher testosterone than those with lower levels. For optimal testosterone production daily vitamin D intake should be between 600-1000 IU but higher doses may be needed in some cases. If you are unsure of your current vitamin D status or how much to supplement, consult a doctor before taking any supplements.
Conclusion
In summary, we need to understand the connection between vitamin D and testosterone. Low levels of either can cause health problems like low energy or libido, depression and even increase risk of certain diseases. To keep you healthy you should eat a balanced diet with vitamin D rich foods (like fish) and exercise regularly. Supplement may be needed if your blood tests show you have low levels of these nutrients. Proper care can provide our body with the necessary vitamin D and testosterone for optimal health.
Check your Vitamin D and Testosterone levels with Discounted Labs. Get your Vitamin D and Testosterone test today without doctor’s visit!
References
- Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Testosterone Levels in Men
- Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Testosterone Levels in Adult Males: A Systematic Review
- Can Vitamin D Restore Low Testosterone Levels?
- Vitamin D Increases Testosterone Production
- Can Vitamin D Increase Testosterone Concentrations in Men?
- 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Testosterone Levels Association Through Body Mass Index: A Cross-Sectional Study of Young Men with Obesity
- Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Testosterone Levels in Men






