What is the Best Testosterone Dose? Results from a Study

Is 2ml of Testosterone a Week Enough to Build Muscle? Study Results
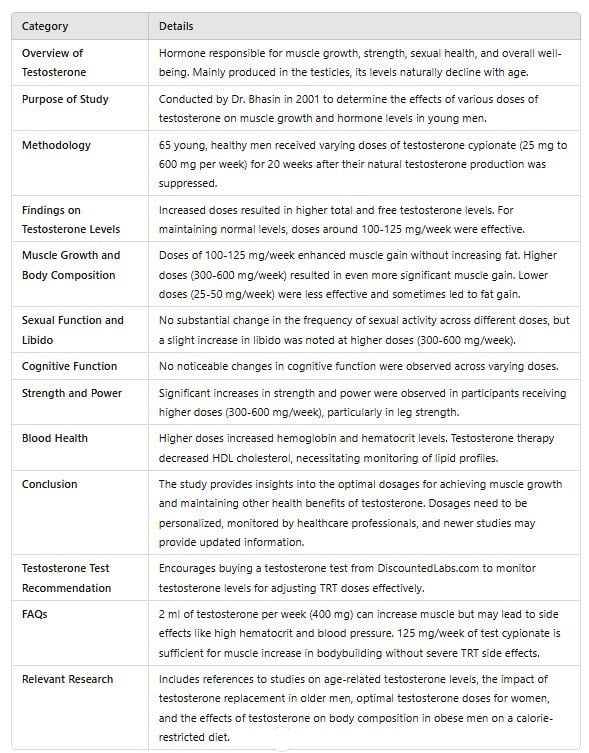
Testosterone is a hormone that plays many roles in the body, like building muscle, increasing strength, sexual health, and overall well-being. People wonder how much testosterone is needed to achieve these benefits, especially when considering testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) for muscle growth. Those with low testosterone might be considering TRT to feel better. But figuring out the right testosterone dose to use is tricky because it depends on your age, health, diet, exercise program, and how your body reacts to the treatment.
In this article we will be looking at a study by Dr. Bhasin and his colleagues in 2001 published in the American Journal of Physiology and Endocrinology Metabolism. Their study was to see how different amounts of testosterone affect young men and what’s the best dose for different results. By going through what they found out we can learn a lot about what’s the right amount of testosterone for getting stronger or building muscle.
Watch video here: What is the Optimal Testosterone Dose?
Testosterone and Muscle Growth
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a big role in muscle growth and development. Produced mainly in the testicles in men, testosterone is responsible for the development of male characteristics, including muscle mass and strength. As men age, their testosterone levels decline naturally, which can lead to a decrease in muscle mass and strength. This decline can affect overall health and well-being, so it’s important to understand the connection between testosterone and muscle growth.
For those who want to build muscle, maintaining optimal testosterone levels is crucial. Testosterone stimulates protein synthesis, which is the process by which the body repairs and builds muscle tissues. Higher testosterone levels can increase muscle mass, strength, and overall health. By understanding how testosterone affects muscle growth, you can make informed decisions about your fitness and health goals.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) for Muscle Growth
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a treatment for those with low testosterone. TRT involves injecting, gelling, or patching testosterone to restore normal testosterone levels. This is especially good for those experiencing symptoms of low testosterone such as decreased muscle mass, fatigue, and decreased libido.
TRT can increase muscle mass and strength, bone density, and overall health. By restoring testosterone levels, TRT supports the body’s natural ability to build muscle and perform physically. But please note that TRT should only be done under the guidance of a doctor. While TRT can be beneficial, it also has side effects and risks, like increased red blood cell production and changes in cholesterol levels. So medical supervision is necessary to ensure safe and effective treatment.
The Study
In the study, about 65 young men around 25 years old and in good shape were studied. The study also included 1 ml of testosterone as part of the dosage variations. First they stopped their bodies from making testosterone naturally by giving them a drug that blocks testosterone. Then for 20 weeks they gave these men shots of a type of testosterone called cypionate once a week. The dose varied from 25 milligrams to 600 milligrams a week. By doing this, they could see how different doses affect different things.
Testosterone Dose and Hormone Levels
The study found a correlation between the dose of testosterone and the levels of different hormones in the body. They looked at total testosterone, free testosterone, LH (luteinizing hormone), SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin), and IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1). Here’s what they found out:
-
As the dose of testosterone increased, so did the total testosterone levels in the body. At the beginning, the subjects had testosterone levels of 500-600 ng/dL. By week 16, those who got higher doses (300-600 mg/week) had levels of 1300-2300 ng/dL. Even with a smaller dose of 125 mg/week, the subjects had levels near what they started with. So taking around 100-125 mg/week might be enough for young men to get their testosterone back to normal.
-
Free testosterone: Just like total testosterone, as more was given, free testosterone increased. So more dosage means more free testosterone is available in your system.
-
LH and SHBG: The more testosterone you take, the lower these levels go. As people increase their dose of testosterone, they see a drop in LH and also in SHBG. So taking more testosterone can slow down LH production and decrease SHBG. So more free testosterone is available for your body to use.
Testosterone dosage for muscle growth and body composition
The study looked into how different doses of testosterone affect muscle building, muscle size, and body composition. They used various methods to measure lean muscle mass (fat-free mass) and body fat. Here’s what they found out:
-
For fat-free mass, the study found that 100-125 mg of testosterone per week helped people gain muscle without fat. Those who took these doses had less body fat and more muscle. Even more (300-600 mg/week) gave better results in gaining muscle without fat. But the smallest doses (25-50 mg/week) didn’t do much; sometimes they even added fat.
-
For body fat, it seems that higher doses help reduce it. Those who got 100-125 mg per week lost body fat. Those who got very low doses (25-50 mg/week) didn’t lose weight or might have added body fat. So high levels of this hormone can make you leaner by cutting down fatty tissues while increasing muscle growth.
Factors to Consider in Testosterone Dosage
Determining the right testosterone dosage for TRT involves considering age, health status, and individual goals. Age is a big factor, as older men may need different dosages than younger men due to natural hormonal decline. Men with underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease or metabolic disorder may need customized dosages to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Individual goals also matter in determining testosterone dosage. For example, someone looking to improve overall health may need a different dosage than someone looking to gain massive muscle and bodybuilding. Personalized treatment plans are necessary to address these individual needs and goals.
Working with a doctor is key to determining the right dosage. Regular blood tests and monitoring can help adjust the dosage as needed to keep testosterone levels within normal range. By considering these factors and working with a medical professional, you can get the best out of your TRT.
Testosterone Dose and Sexual Function and Libido
The study also looked into how different doses of testosterone affect sexual function and desire. To find out they asked participants to fill out questionnaires about their sex life and how much they wanted sex. Here’s what they found out:
-
For sexual activity, the study didn’t show much change in how often people were sexually active when they took more testosterone. The frequency of sexual encounters remained the same across all doses. Note that there were not many participants in this study, so this might have affected the results.
-
For libido, it was found that 300-600 mg/week of testosterone gave a slight increase in desire. But 25-125 mg/week didn’t make much of a difference in libido. So higher doses used by bodybuilders might be more effective in increasing sexual desire.
No Change in Cognitive Function
In the study they also looked into how well people can think and remember. But even with different doses of testosterone, there was no big change in brain function. Note that this study was done on young guys. To know if testosterone affects thinking and memory in older men more studies need to be done.
Testosterone Dose and Strength and Power
In the study they tested the strength and power of participants’ legs by having them do leg press for 20 weeks. What they found out was interesting—the amount of testosterone given to the participants made a difference in how much stronger or more powerful their legs became. Those who got 300-600 mg/week had a significant increase in strength and power of their legs. So taking higher doses of testosterone can make you stronger and more powerful even if you don’t work out.
Hemoglobin, Hematocrit and Cholesterol Levels
Giving testosterone changes blood counts and fat levels in the body. The results match what we already know:
-
Hemoglobin: As testosterone dose increased, so did hemoglobin levels. So as more testosterone is given more hemoglobin goes up. This means treatment with testosterone can affect erythropoiesis, which is how our body makes red blood cells.
-
Just like hemoglobin, when testosterone doses go up, so does hematocrit. Hematocrit is all about how much space red blood cells take up in our blood. The study didn’t specify what’s the ideal level of hematocrit is, but note that too much can be bad for your heart health.
-
Lipid Profile: The administration of testosterone caused a fluctuation in the levels of HDL cholesterol, the beneficial type. When you have more testosterone in your system, your HDL cholesterol tends to decrease. So it’s really important to monitor lipid profiles if you’re on testosterone therapy.
Conclusion
In 2001 Dr. Bhasin and his team did a study that looked into how different doses of testosterone affect several factors. Although the study was done on young men and had a small number of participants, it still gives us valuable information on how testosterone levels relate to muscle size, sexual health, brain function, physical strength, and blood-related measures.
According to the study, 100-125 mg/week may be enough for young men to get their testosterone levels back to normal. For bodybuilding, 300-600 mg/week seems to increase muscle size, strength, and sex drive. But we have to remember that people react differently to each other. So any treatment with testosterone should be customized for each person’s needs and monitored by a healthcare professional who knows what he’s doing.
Note that the study was done more than 20 years ago. Since then there might be new findings. If you’re thinking of testosterone therapy, talk to medical experts. They can assess your situation and give you personalized advice.
The study provides valuable insights into the functioning of testosterone dosing, highlighting the need for further investigation. By doing more research, we can make the most of testosterone therapy and minimize the downsides.
Get a budget-friendly testosterone test without seeing a doctor.
Buy a testosterone test from DiscountedLabs.com and find out your testosterone blood level and adjust your TRT dose.
FAQs
Is 2 ml of testosterone a week enough to build muscle?
The study above showed that 125 mg/week of injectable testosterone was enough to increase muscle. 2 ml of testosterone is 400 mg/week which will increase muscle but may cause high hematocrit, water retention, and blood pressure.
How much test cypionate a week for bodybuilding?
The study above showed that 125 mg/week of test cypionate is enough to increase muscle in bodybuilding without TRT side effects.
References:
-
In a study titled "Age trends in the level of serum testosterone and other hormones in middle-aged men: longitudinal results from the Massachusetts male aging study", researchers looked at how hormone levels, including testosterone, change as men get older.
-
The article "Testosterone Replacement in Older Men: A Clinical Perspective" discusses the benefits and considerations of giving older men testosterone to improve their health.
-
According to research found on Harvard's website, scientists have figured out what dose of testosterone works best for women.
-
Another study called "Effects of Testosterone Treatment on Body Fat and Lean Mass in Obese Men on a Hypocaloric Diet: A Randomized Controlled Trial" explores how taking testosterone can help obese men lose fat but keep muscle while eating fewer calories.





