DHEA Supplement: Is It Right for You?
DHEA Levels: Do You Need to Take a Supplement?
The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) test checks how much DHEA-S is in the blood. The adrenal gland produces the hormone DHEA-S. It is a building block for androgens and estrogens. The test is generally done to check how well the adrenal glands are working and to look into conditions that might cause hormone production to be off.
DHEA-S test, also known as the test DHEA sulfate, can help figure out what’s causing irregular periods, infertility, and a low libido. It is also used to find out if someone has a growth in their adrenal gland, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, or polycystic ovary syndrome. People on long-term glucocorticoid medicine can also use the test to check how well their adrenal glands are working. It is an important test for people who think their hormones might be out of order.
What is DHEA?
The adrenal glands also produce dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), the most abundant hormone found in the blood stream. Your adrenal glands and, to a lesser extent, your ovaries and testes produce the hormone known as DHEA. DHEA is changed into DHEA-S in your adrenal glands and liver.
The body uses DHEA as the starting material for producing the sex hormones testosterone and estrogen. However, DHEA supplementation studies have shown that it only increases testosterone in women. The production of DHEA diminishes in most people after age 40. DHEA levels typically decrease with age in both men and women, highlighting its significance in hormone testing and the evaluation of conditions affecting adrenal function and hormonal balance. In people aged 70 years, DHEA levels will be approximately 30 percent lower than what they were at age 25. Low blood levels of DHEA have been associated with many degenerative conditions, making it a popular supplement for those undergoing in-vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments.
Understanding DHEA and Its Role in the Body
DHEA is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, which are small glands located on top of each kidney. These glands are responsible for producing most of the body’s DHEA, with smaller amounts being produced by the testicles in men and ovaries in women. DHEA plays a crucial role in the production of sex hormones, including testosterone and estrogen, which are essential for the development of male and female sex characteristics.
As we age, DHEA levels naturally decline, with the highest levels typically occurring during puberty. This decline can lead to a range of symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, and weight gain. However, it’s important to note that DHEA supplements are not recommended as a way to prevent aging-related conditions, as there is no reliable evidence to support their effectiveness. While some people may seek out DHEA supplements to counteract these symptoms, it’s crucial to approach supplementation with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
DHEA is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands
DHEA plays a crucial role in the production of sex hormones
DHEA levels naturally decline with age
The Importance of DHEA Sulfate (DHEAS)
DHEAS is the most abundant form of DHEA in the body, accounting for approximately 90% of the total DHEA present. Produced by the adrenal glands, DHEAS is converted into DHEA in the body. The DHEA sulfate test measures the levels of DHEAS in the blood, which can help diagnose adrenal disorders and evaluate adrenal function.
DHEAS plays a crucial role in regulating the reproductive system. Abnormal levels can lead to a range of symptoms, including excess hair growth, male pattern baldness, and deepening of the voice in women. In men, high levels of DHEAS can cause early puberty, while low levels can lead to erectile dysfunction and decreased libido.
In women, high levels of DHEAS can cause polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess hair growth, and infertility. Low levels of DHEAS can lead to adrenal insufficiency, a condition where the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones.
The DHEA sulfate test is typically ordered by a healthcare provider if symptoms indicate an adrenal disorder or adrenal tumor. The test involves a blood sample, which may cause moderate pain, a prick or sting, and possibly some throbbing or bruising after the needle is inserted. The test is usually performed at a doctor’s office or another medical setting, and the results are typically available within a few business days.
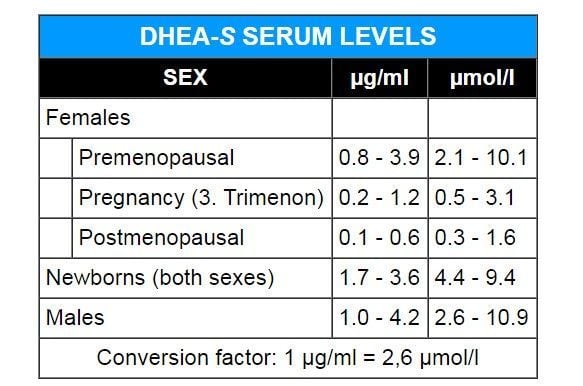
Normal blood levels of DHEAS can differ by sex and age, with typical normal ranges for females being 20-150 mcg/dL and for males being 30-450 mcg/dL. Abnormal levels of DHEAS can indicate a range of conditions, including adrenal gland disorders, pituitary gland disorders, and congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
In conclusion, DHEA and DHEAS play crucial roles in the body, and abnormal levels can lead to a range of symptoms and conditions. The DHEA sulfate test is an essential tool for diagnosing adrenal disorders and evaluating adrenal function. If you’re experiencing symptoms related to adrenal disorders, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
DHEAS is the most abundant form of DHEA in the body
Who Can Benefit from Taking DHEA Supplements?
Some controversial and non-conclusive studies have shown that people with immune deficiencies and fatigue may benefit from supplementation with this hormone. It is also believed to help correct some adrenal problems, such as changes in blood pressure, caused by conditions such as adrenal insufficiency. It is still available over-the-counter in the United States. Due to a recent congressional bill classifying it as a performance-enhancing steroid (despite the fact that no studies have demonstrated that it has such an effect), this might soon change.
One study showed that women with the correct levels of DHEA can convert it into testosterone as their body needs it, while men do not benefit to the same degree. You need a blood test to know if you have low DHEA-S since most of the DHEA converts into this sulfated form. Common doses for women are 5 to 30 mg a day, while men tend to benefit from 25–100 mg per day (to bring low levels of DHEA-S to normal)
DHEAS was the only hormone significantly negatively correlated to the prevalence of erectile dysfunction among 17 investigated hormones, including testosterone and estradiol, in the large and long-term Massachusetts Male Aging Study. In addition, a study done by Dr. Basar et al., which included 348 male patients, reported that DHEAS and free testosterone levels were significantly lower in men with sexual dysfunction. However, evidence of the positive effects of DHEA supplementation on improving sexual function in men is unconvincing, scanty, and conflicting. Only 4 placebo-controlled studies have been performed to investigate the effect of supplementing DHEA on improving libido in men. Unfortunately, the data from these studies did not show any difference in sexual desire in men. The limited effect of DHEA on male sexual function is not surprising. In fact, the specific DHEA contribution to the overall circulating testosterone level in men is marginal, if not negligible.
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study was done on male and female patients with low thyroid function (hypopituitary) who were given growth hormone (GH) along with 50 mg of DHEA. When DHEA was replaced in female patients, the dose of GH dropped by 14.6 +/- 20% while serum IGF-I stayed the same (P < 0.05). This was maintained for 12 months, and there was a significant fall in serum IGF-I two months after the withdrawal of DHEA. There was no change in the male group.
Do not use DHEA supplements unless your blood levels of DHEA-S are low. If low, start at a low dose and get your DHEA-S tested again after a month. Men who use DHEA supplements may have problems with higher estrogen levels since this hormone can also be metabolized into estradiol. This could result in gynecomastia and water retention. If you start taking DHEA, have your blood levels checked to make sure they are not above normal. Additionally, individuals with a history of hormone-sensitive cancers, such as breast or prostate cancer, should consult with their doctor before taking a DHEA supplement. There are many claims about DHEA being an anti-aging and anti-cancer cure, but none of these claims have been substantiated with strong data.
How Do You Know Your DHEA Blood Level with a DHEA Sulfate Test?
The standard blood test to evaluate DHEA status is one that measures DHEA sulfate levels (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, or DHEA-S). DHEA-S is calculated in micrograms per deciliter (µg/dL) of blood. A DHEA-S blood test may be taken three to six weeks after initiating DHEA to help determine optimal dosing. DHEA testing may save you money if it shows you can take less DHEA to maintain youthful DHEA serum levels.
Potential Benefits of DHEA Supplementation
Low DHEA and Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough of the hormone DHEA. In such cases, doctors may prescribe DHEA supplements to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. The National Collegiate Athletic Association has banned the supplement, but studies have shown that it may be useful in treating lupus and adrenal insufficiency (Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier). However, further research is still needed to determine its effectiveness in treating these conditions.
DHEA and Depression
DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) supplements have been studied for their potential to alleviate depressive symptoms. The test DHEA sulfate can help diagnose adrenal disorders that may contribute to depressive symptoms. Studies have found that DHEA-S levels are associated with depressive symptoms in women in the late reproductive years. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials showed that DHEA may be effective in treating depressive symptoms in various psychiatric and medical illnesses. However, further research is needed to fully understand the effects of DHEA on depression and its potential as a treatment option, making DHEA treatment a potential option for those struggling with depressive symptoms.
DHEA in Elderly Men
A DHEA supplement has been found to be beneficial for elderly men. Studies have shown that elevated serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate levels correlate with an increased risk for metabolic syndrome in elderly men. DHEA supplements can also produce small decreases in fat mass in elderly men, although more research is needed to confirm this finding. Additionally, taking DHEA supplements may also have an effect on body weight and fat burning, but the evidence is unclear. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before taking any DHEA supplements, especially for elderly men with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications.
DHEA supplements have been suggested to slow down the aging process by maintaining DHEA levels in the body. Although some small studies have reported positive anti-aging effects from the use of DHEA supplements, others have not shown any effect. According to the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database, there is no conclusive evidence that DHEA supplements affect the aging process. DHEA is a precursor for the production of estrogens and androgens, and its production decreases with the aging process, which makes it a controversial topic among researchers regarding its use in postmenopausal women.
DHEA and Bone Density
A DHEA supplement has been studied for its potential to improve bone mineral density in older women. Studies have produced mixed results, but some suggest that DHEA may increase bone mineral density in the hip and thigh bones of females. This effect seems to increase with higher doses of the supplement. DHEA can be expressed via sex steroid receptors and androgen and estrogen receptors and plays a role in bone cell proliferation and differentiation. The activation of androgen receptors can stimulate bone cell growth, which may contribute to improvements in mineral density.
DHEA and Bodybuilding
DHEA often gets marketed as a “muscle builder” to men. As a muscle-building supplement in young, healthy men, DHEA is essentially worthless, and high intakes may in fact be counterproductive to gaining muscle as high doses also cause an increase in estrogen and the effects on testosterone are minimal. Studies have been conflicting in this area at best, and most “real world” users report no improvements in strength, muscle mass, etc. from using DHEA, with little evidence to support its effectiveness.
As a supplement that can improve mood, libido, memory, and possibly alter body composition (i.e., increase muscle, improve bone density, and reduce body fat), DHEA appears to be an option to explore for women. Most of the research has been done in DHEA-deficient populations, but data and real-world experience suggest it's also beneficial to women who are not medically deficient in this hormone, particularly in improving sex drive. Although the benefits of this hormone to women come predominately from its conversion to testosterone, it also appears that some of the effects may be due to other mechanisms.
DHEA Potential Interactions
Yes, it is important to be aware of potential interactions with other medications or supplements when taking a DHEA supplement. DHEA can interact with several types of medications like blood thinners, insulin, and corticosteroids. It may also affect the effectiveness of certain herbal supplements, like ginkgo biloba and saw palmetto. People with liver problems should also avoid taking DHEA, as it is metabolized in the liver. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure there are no adverse effects or interactions with existing medications or supplements.
How Long Does It Take for DHEA to Work?
The length of time it takes to see results from taking a DHEA supplement can vary depending on multiple factors. Some people may notice an improvement in their symptoms within just a few days, while others may need to take the supplement for several weeks or even months before seeing any noticeable changes. It is important to speak with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the appropriate dosage and monitor any potential side effects. Additionally, it's important to keep in mind that DHEA supplements are not appropriate for everyone and that those who are pregnant, nursing, or have certain medical conditions should avoid taking them.
DHEA Dosage
The recommended dosage for a DHEA supplement varies depending on age, gender, and health conditions. Generally, the recommended dosage for men is 50–100 mg per day, while women are advised to take 25–50 mg per day. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen. Additionally, it is recommended to take DHEA supplements in the morning as the body naturally produces more DHEA during this time. It is also suggested to cycle DHEA use, taking it for three weeks and then pausing for one week before resuming.
different individuals. Its role in supporting adrenal function, potentially aiding in conditions like adrenal insufficiency and depression, and influencing bone density and sexual health, offers hope for specific groups, especially postmenopausal women and the elderly. However, it's crucial to approach DHEA supplementation with caution and informed understanding. Men, particularly, may find limited benefits and should be wary of potential side effects like increased estrogen levels.
Conclusion
Before considering DHEA supplements, it's essential to get your DHEA-S levels tested. This is where DiscountedLabs.com can be an invaluable resource, offering affordable and convenient blood tests without the need for a doctor's visit in several U.S. states. Understanding your DHEA-S levels is the first step in determining whether supplementation is right for you.
Remember, while DHEA has potential benefits, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. Consult with healthcare professionals, consider potential interactions with other medications or supplements, and monitor your body's response to supplementation. As we continue to explore the benefits and limitations of DHEA supplements, it's essential to make informed, health-focused decisions, aided by reliable testing and professional advice. Turn to DiscountedLabs.com for your testing requirements if you're thinking about taking DHEA supplements so that you can make informed health decisions.





